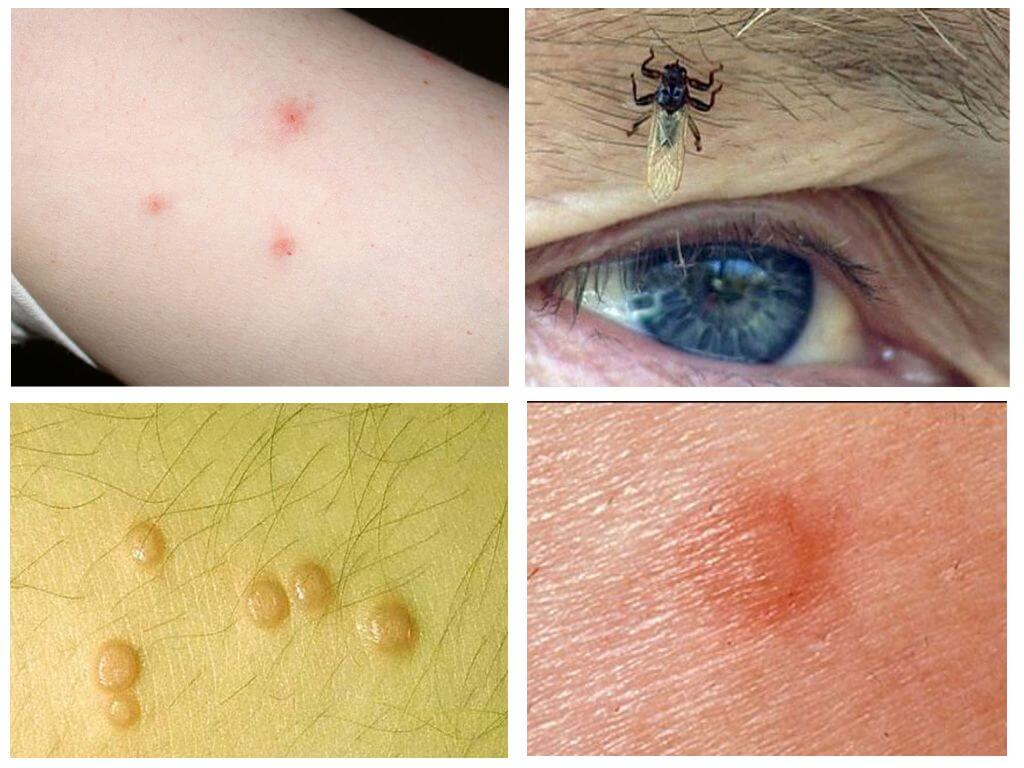
Bloodsucker deer (elk flea, fly, louse, tick)
Content
- Deer bloodsucker
- Deer bloodsucker
- Deer bite
Entomologists do not distinguish such species as elk flea. However, in everyday life, this concept applies to all blood-sucking insects that have chosen large horned animals as breadwinners: roe deer, deer, elk. Articles and smaller warm-blooded representatives of the fauna as well as humans can be victims of parasites.
What moose fleas look like
Elk fleas live in northern Europe, Scandinavia, and Siberia. Most often they are found in the taiga and in the cold regions of Russia. Elk fleas are called several insects:
- goat fleas;
- deer bloodsucker;
- alakurt
All parasites belong to different sub-orders and have their own characteristics. Below are elk fleas in the photo. To understand which danger to humans and animals are bloodsuckers, it is worth considering each of them separately.
Features parasitism deer bloodsucker
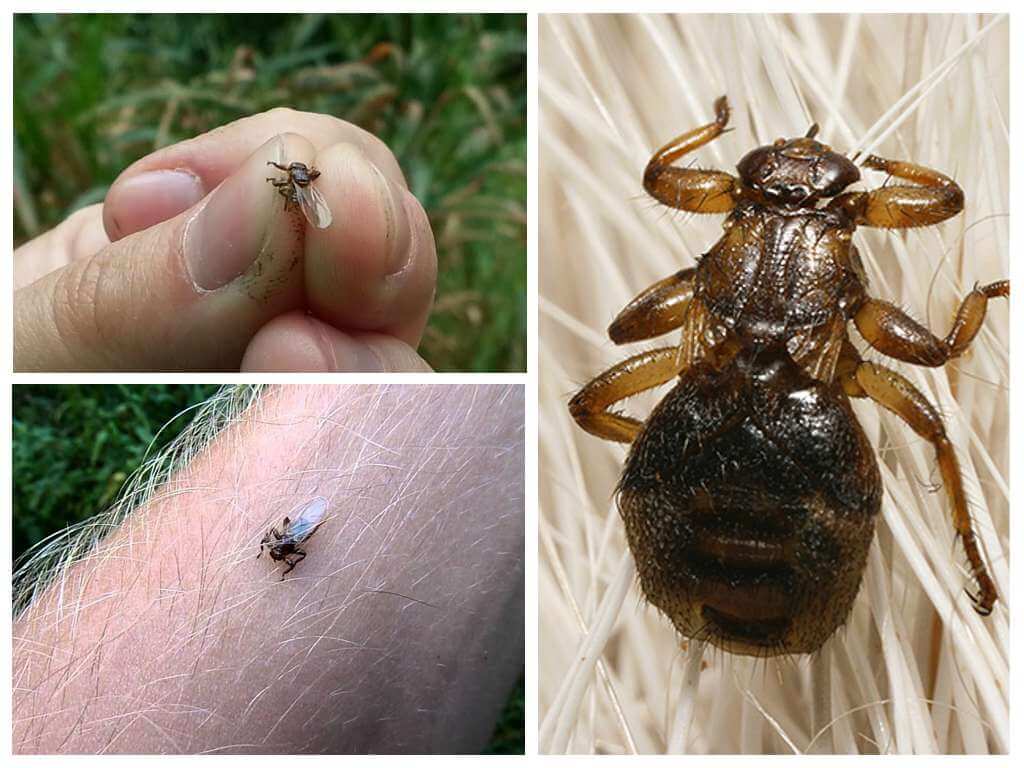
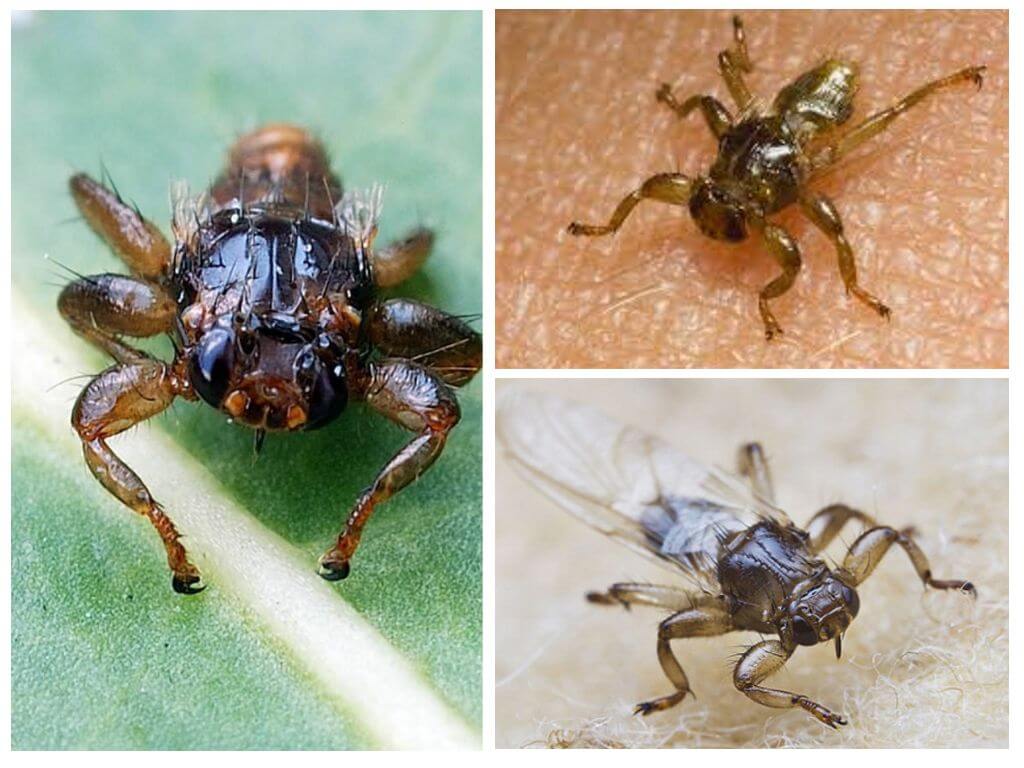
Deer sucker is a large sized annoying fly. It is also called a flea, louse, tick. Flat flat body with a strong chitinous cover allows the insect to withstand strong physical pressure, so crush it is not so simple. The size of the bloodsucker does not exceed 3.5 mm. The characteristic light brown shiny color highlights the fly from elk fleas.
The insect is characterized by strongly developed wings, but it is not capable of long flights. On a thickened head are large eyes, occupying 25% of the entire surface. Mouth apparatus piercing-sucking type involves feeding only with blood.During the day, the bloodsucker does up to 15 meals, each time drinking up to 1.5 mg of blood. The parasite is very tenacious and adapts to any warm-blooded, on which it parasitizes. Mostly wild animals are attacked.
On the body of one moose can be concentrated up to 1000 copies. On average, 200-300 flies constantly inhabit the animal. Bites very painful, cause itching, anxiety. Redness and rash appear in their place. It was experimentally established that the elk fly prefers thick wool and therefore most of them are concentrated in the neck and back.
On a note!
With a large population of people, people also become victims of deer bloodsucker. There are cases when 100-120 individuals attacked a person in one minute.
A moose louse hunts during the daytime. It is interesting that she does not attack children. Such selectivity is due to the size of the sacrifice, because deer bloodsuckers prefer larger carriers. Insect attacks are most often experienced by hunters during the division of prey.
Sticking into the body of its victim, the insect folds its wings, swells up and firmly sticks to the skin, for which it received the popular name - elk tick.
Breeding elk mites
Deer bloodsucker identifies its prey by smell and heat. The tick waits for its donor in the grass or bushes, seeing that a suitable object flies over it and firmly clings to the coat. Features of life in the forest do not allow the bloodsucker to constantly change the owner, so she leads a sedentary lifestyle. Having settled in wool, the tick breaks off its wings and proceeds to parasitism.
Interesting!
For this species tend to live in pairs. The female and male are always kept together. After mating, the female needs constant nutrition and absorbs more blood than the male. Live moles are characteristic of elk ticks. In the abdominal cavity of the female individual larvae, which are called puparia, form.
Over the course of her entire life, the female lays up to 30 puparia, which gradually roll out of the animal's fur and often become food for birds. The peak of breeding activity of elk ticks falls to the end of autumn, the beginning of winter. With the onset of spring, deer bloodsuckers die.
What are dangerous bites deer bloodsucker for humans?
Elk ticks do not tolerate any dangerous or deadly viruses. Harm bloodsucker for humans is painful bites.Numerous attacks of parasites provoke the appearance of a rash, swelling, itching, and allergic reactions.
The following measures will help to protect yourself from attacks by deer bloodsucker in the forest:
- wear protective clothing made of thick fabrics with long sleeves;
- for the protection of the face use a bed fly;
- use powerful repellents that repel forest fleas;
- periodically check the skin for the presence of elk mites;
- on returning home, take a bath with tar detergent.
If elk flea bites deliver severe pain, then the bite sites must be disinfected with iodine solution or alcohol tincture. To relieve itching, ordinary ice will help, and to relieve inflammation and swelling, you should use pharmacy ointments. If the condition worsens and severe allergic reactions appear, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
Tian Shan flea alakurt
Tien Shan elk flea is large. There are individuals whose length in the fertilized form reaches 9-10 mm. In males, the body is concave, whereas in females, after fertilization, the body swells in length and takes on a worm-like appearance.For such a characteristic feature, a flea is called a black or white worm.
At the end of October, after the snow falls from the plants, black worm-like fleas begin to fall off the ground. Severe frost does not prevent their reproduction.
On a note!
As their victim, parasites choose cattle. Sick weak animals do not attract them.
Unlike most species of fleas, alakurt is forced to live on the body of the victim permanently. In this, it is very similar to lice. On one donor there may be numerous accumulations of Tien Shan fleas. Red bloody streaks appear on the animal's body, severe exhaustion sets in, which ultimately often leads to the death of the victim, on which the colony of alakurt settled.
There have been no cases of Tian Shan flea attacks on humans.