What is Lyme disease, its symptoms, treatment and photo
Content
- 1 Discovery history
- 2 Pathogens and vectors
- 3 Spread of borreliosis
- 4 Stage of the disease
- 5 Symptoms of borreliosis
- 6 Stage 2: Symptoms and Treatment
- 7 3rd stage: chronic
- 8 Diagnosis of borreliosis
- 9 Lyme Disease Treatment
- 10 Lyme Disease in Children
- 11 Traditional methods of treatment
- 12 Lyme disease prevention
- Lyme Disease or Tick-borne Borreliosis
- Symptoms of borreliosis
- Stages of development of borreliosis
- Symptoms of chronic stage of borreliosis
- Antibiotics for Borreliosis
- Borreliosis in children
Borreliosis or Lyme disease - an infectious disease that is common in a particular area where pathogens live, it is transmitted through the bites of ixodid mites. As the disease progresses, the symptoms and treatment of Lyme disease, complications and treatment methods depend on the victim’s immune system and the time for seeking medical help.
Discovery history
The medical name for this disease is systemic tick-borne borreliosis, less commonly referred to as erythemal spirochetosis, meningolar neuritis, etc.
Important!
The main difference of the disease is its method of transmission the only way: through the bite of the ixodus tick. Infection from a sick person to other people is not transmitted, which makes it absolutely safe for the family and others.
The official name was given by the name of its pathogen, which is of the type of spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi. And such a name as Lyme disease became known in international medicine after a severe outbreak of infection among residents of Lyme in 1975, recorded in 1975. Connecticut (USA). After a study of scientists conducted in children with juvenile arthritis, the symptoms were first described and pathogenic organisms were sown that caused the disease.
Pathogens and vectors
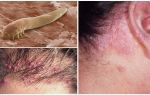
Borreliosis pathogens are 3 types of Borrelia (Borrelia burgdorferi, Borrelia garinii, Borrelia afzelii) - small pathogenic microorganisms no larger than 20 microns in size, similar to a twisted spiral and related to spirochetes. In nature, carriers of bacteria are wild and domestic animals: deer, cows, sheep, horses, goats, rodents, birds, etc.
In European countries, carriers of Lyme disease are certain types of ticks: Ixodes ricinus and Ixodes persulcarus, and in the US and Canada - Ixodes dammini.
On a note!
When a parasite bites an infected animal, Borrelia enters its body, causing it to become a lifelong carrier of the disease. And the tick itself is not sick of it. After he bites his victim, along with saliva, borrelia are injected into the body, which enter the bloodstream and infect a person.
Spread of borreliosis
Lyme disease is spread only in the Northern Hemisphere, where there are mixed deciduous forests and mites. Foci of infection recorded in the United States and Canada, some countries in Western and Eastern Europe. There are also outbreaks of Lyme disease in Russia, Ukraine, Moldova, Lithuania, Estonia and Latvia.
In some countries where there are natural foci of borreliosis, almost 90% of ticks are infected, which spread the infection. Moreover, parasites become carriers for life, and female ticks transmit spirochetes even to their larvae, which from the moment of birth become able to spread borrelia.
On a note!
The most dangerous period for people who may be infected with such an infection after being bitten by ticks is in the warm months of the year: from May to September, the period of maximum activity of the parasites.
Stage of the disease
After a tick bite and penetration of Borrelia under the human skin, they enter the nearby lymph nodes, where they actively proliferate. Within a few days, the bacteria pass into the blood and are carried by vessels throughout the body. At the same time, they continue to multiply, gradually affecting the nervous, cardiovascular systems, joints and muscles.
On a note!
The reaction of the victim’s immune system is usually acute: antibodies are produced, but they are not capable of eradicating the infection completely. Most often, borreliosis disease becomes chronic, in which the patient's condition gradually worsens due to an increase in the autoimmune process and the constant release of toxic substances.
The incubation period, i.e.The time until the first negative symptoms appear is from 3 to 32 days. Most often the disease manifests itself 1-2 weeks after the tick bite.
Tick-borne borreliosis (ICD code 10-A69.20) proceeds in 3 stages:
- Reproduction of Borrelia under the skin and in the lymph nodes, its duration is up to 40 days.
- The phase of active propagation of pathogenic bacteria through the circulatory system throughout the human body, which lasts 5-6 months.
- Chronic borreliosis, in which damage to the nervous, musculoskeletal or cardiovascular systems occurs, lasts for several years.
At each stage, there are certain symptoms for which specialists can clearly diagnose the disease.
Symptoms of borreliosis
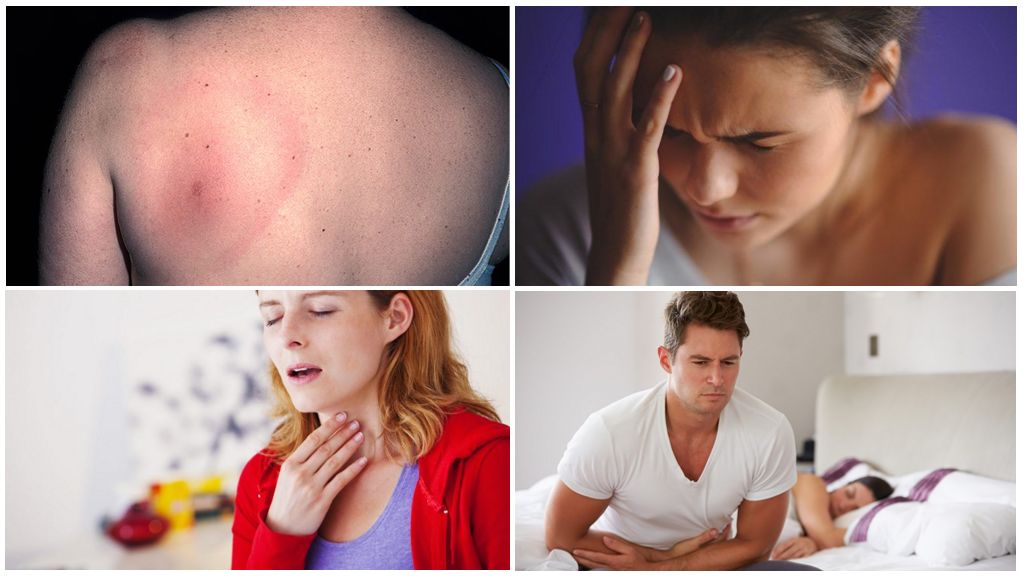
The general and specific manifestations of stage 1 disease are as follows:
- headache, temperature rises to + 38 ° C, chills;
- migratory pains and aches in joints and muscles;
- nausea, vomiting;
- soreness and an increase in the lymph nodes;
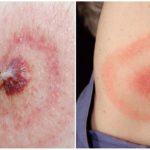
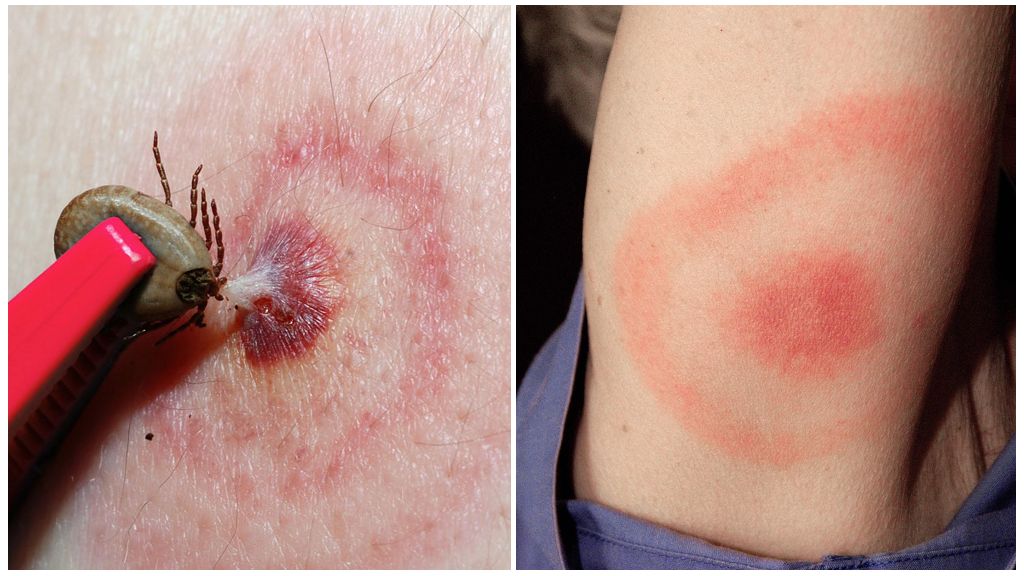
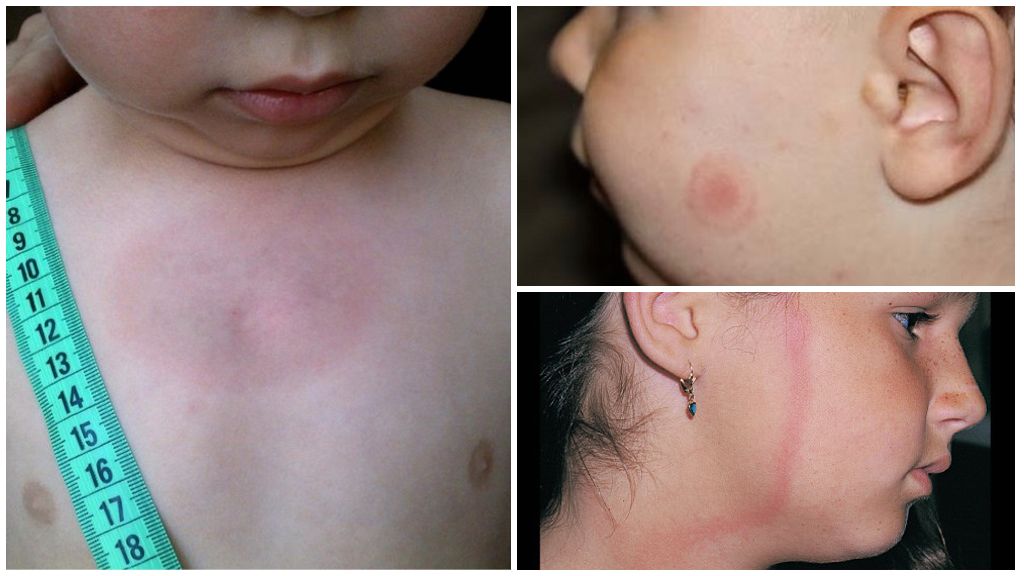
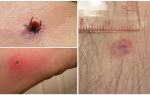
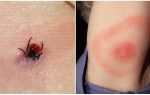
- the appearance at the site of the bite annular erythema, which is a specific symptom and allows you to identify Lyme disease at the beginning;
- rarely possible rash with borreliosis throughout the body, conjunctivitis;
- sore throat, cough, runny nose.
Erythema in patients with borreliosis is diagnosed in 70% of cases. It is characterized by the formation of a red-colored papule seal at the site of the tick bite. It gradually expands in diameter and takes the form of a brightly defined ring raised above the skin. The center becomes more pale, and the bezel acquires a rich red color. The area of erythema in tick-borne borreliosis (photo below) can reach from 10 to 60 cm. Occasionally, there are several red rims.
In very rare cases, the disease is asymptomatic, that is, without the appearance of erythema and other signs. Often, an infected person does not feel any discomfort due to the appearance of erythema, but sometimes it can hurt, burn, or itch. It is also possible the appearance of secondary red rings in areas where there were no tick bites.
Erythema can persist on the patient's skin for a long time, on average 30 days, sometimes it goes away within a few days. In some patients, rings are visible on the body, even after several months. After the disappearance of the skin remains pigmentation, dryness and peeling.
Important!
If a sick person has not paid attention to the initial negative symptoms of Lyme disease after a tick bite, then they can go away even without using medications.However, then the disease passes into the 2nd stage, more severe, in which the health risk increases.
Stage 2: Symptoms and Treatment
At the next stage of ixodic tick-borne borreliosis, the main systems of the diseased person are affected.
Typical syndromes of the nervous system:
- signs of serous meningitis (inflammation of the lining of the brain), which are characterized by: headaches photophobia, tension of the occipital muscles, fatigue, high sensitivity to some stimuli, insomnia, impaired memory and attention, emotional disorders;
- nerve damage occurs in the cranial region of the brain: paralysis of facial muscles, hearing, vision, strabismus, or eye movement disorders;
- radiculopathy or damage to the roots of the spinal nerves, which is clinically manifested in "lumbago" pain in the lumbar region or limbs, muscular weakness gradually develops, tendon reflexes are disturbed.
Important!
In 10% of patients with borreliosis, speech disorders, movement instability, limb tremor,difficulty in swallowing.
Borreliosis is manifested by complications in other important systems of the patient's body with certain symptoms:
- damage to the joints, which is expressed in recurrent arthritis in the knees, elbows, hip or ankle, which leads to pain and reduced mobility of the joints;
- Borrelia penetration into the cardiovascular system is manifested in the appearance of symptoms of myocarditis, pericarditis: heart failure, frequent heartbeat, shortness of breath, pain in the chest and behind the sternum;
- signs of skin lesions: rash similar to urticaria, secondary ring erythema, lymphocytomas - bright red nodules ranging in size from 3 mm to 5 cm, which rise above the skin surface, they can appear on the ear lobe, in the groin or on the nipples of the breast.
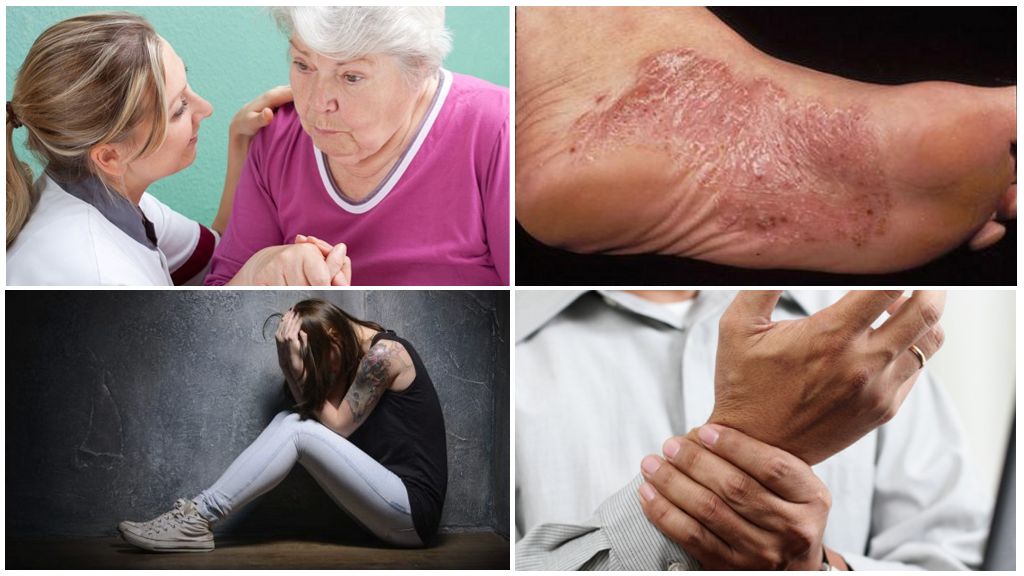
3rd stage: chronic
The last stage of borreliosis develops several months after the first signs of the disease. It is characterized by the development of chronic Lyme disease, in which one of the main systems of the patient is affected.
Typical symptoms and effects of borreliosis:
- chronic arthritis: the defeat of small and large joints, expressed in their gradual deformation and the development of osteoporosis;
- atrophic acrodermatitis: the appearance on the skin of blue and red spots in the knees, elbows, the inner side of the hands, soles, compaction occurs, and then atrophy and thinning; benign lymphadenosis of the skin;
- diseases of the nervous system: encephalopathy, polyneuropathy and encephalomyelitis, which are manifested in the development of paresis, changes in sensitivity, coordination, deterioration of mental activity (memory, thinking, intellectual abilities), epilepsy attacks, impaired hearing or vision, general lethargy, depression.
Important!
With the wrong diagnosis, the absence of treatment, Borreliosis is dangerous precisely because of its severe complications, which remain with a person for life and often lead to disability. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to your own state of health after an accidental tick bite and to seek the help of doctors in time.
Diagnosis of borreliosis
In cases of suspected Lyme disease, in addition to a general examination of the patient, specialists conduct erythema detection and other specific signs of the disease.When they are detected, clinical studies of blood and tissues are performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Occasionally, there are no external signs of the disease, and laboratory diagnosis is the only reliable way to confirm the presence of the disease.
Borrelia is quite difficult to identify the patient, therefore, using indirect methods, the effectiveness of which reaches 50%.
Basic laboratory methods for identifying Lyme disease:
- hemotest for borreliosis: blood tests for the presence of infection, performed 7-10 days after the tick bite;
- Borrelia DNA search in the blood is done by polymerase chain reaction;
- immune chip for borreliosis - a study of blood serum using a diagnostic test system developed in the Russian Central Research Institute of Epidemiology allows determining antibodies in the blood to 8 groups of borrelia antigens that are spread throughout the Russian Federation.
On a note!
To clarify the severity of lesions of various organs of the patient, X-ray and ultrasound examinations, ECG and EEG, puncture of the joints and skin biopsy are used. All patients with Borreliosis undergo quarterly examinations for a period of up to 2 years.
Lyme Disease Treatment
When confirming the diagnosis, patients undergo inpatient treatment in the infectious disease ward of the hospital. In some mild cases, it is acceptable to treat borreliosis at home, but only under the constant supervision of specialists.
The effectiveness of treatment depends on the stage of the disease: in the initial period it is higher. Outpatient treatment can be prescribed if it is confirmed that there is no mixed infection, i.e. there is no infection with encephalitis virus. In the treatment of this disease it is recommended to observe a sparing diet, refrain from alcohol.
Drug treatment of borreliosis is carried out in 2 areas:
- etiotropic, including the impact on the pathogen itself, which is carried out using a course of antibiotics;
- symptomatic - treatment of the affected organs and systems with anti-inflammatory, detoxification, antihistamine, cardio and tonic drugs, complex vitamins.
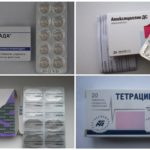
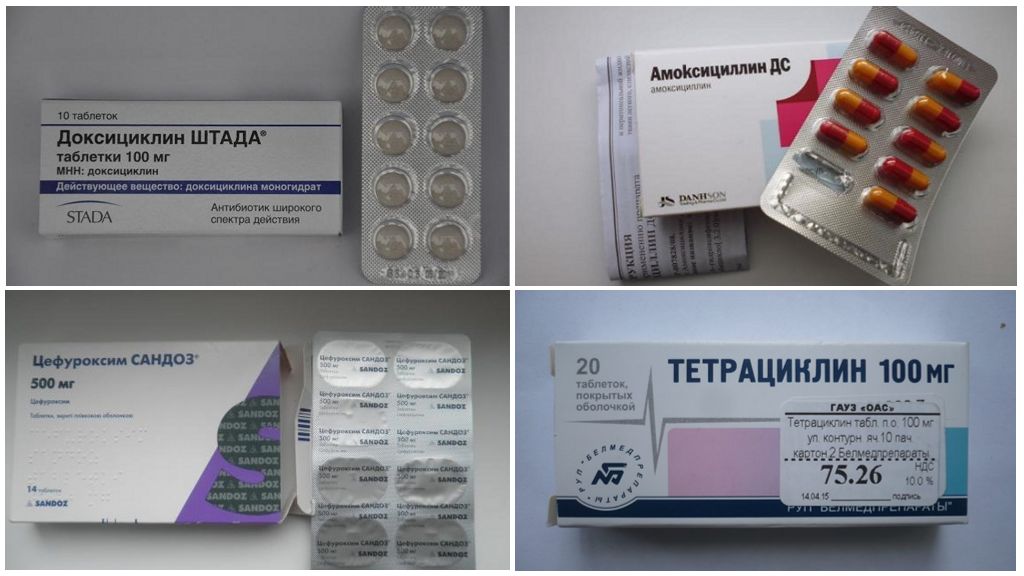
At the 1st stage, the doctor prescribes antibiotics in tablets for borreliosis for 10-14 days:
- Tetracycline (price 50-60 rubles);
- Doxycycline (about 30 rubles);
- Amoxycycline (80-90 rubles);
- Cefuroxime (about 100 rubles).
The prescribed dosage must be adhered to strictly, it is categorically impossible to shorten the course because of the possible survival of some Borrelia. At this stage, the prognosis for cure is favorable: in most cases, adequately administered therapy leads to full recovery.
At stage 2, treatment of borreliosis with antibiotics is already carried out through intravenous injections of Penicillin, Ceftriaxone. The duration of therapy is 2-3 weeks. The probability that the patient is fully cured of Lyme disease is 85-90%.
At stage 3, Lyme disease has been treated with antibiotics for 28 days with the use of penicillin preparations. The most frequently prescribed prolonged form of the drug is Extensillin, which replaces the 8-fold frequency of antibiotic intake per day.
Important!
Pathogenic bacteria of Borrelia remain in the lymphatic system of a person who has been ill for 10 years. You should also be aware that immunity after borreliosis is not produced, so re-infection is possible, even 5-7 years after recovery.
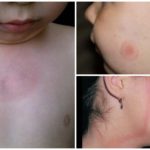
Lyme Disease in Children
In contrast to the course of borreliosis in adults, children in most cases are characterized by damage to the nervous system and the appearance of symptoms of meningitis. Kids up to 7 years old are practically not sick, and in older children the symptoms, clinical signs and manifestations of the disease are similar to the above.
After recovery in young patients, negative reactions may remain in the form of sleep disorders, unstable mood and increased nervous irritability. All these unpleasant effects of borreliosis after some time pass.
Traditional methods of treatment
In the medical treatment of Lyme disease, adherence to a special diet and the intake of products that normalize the intestinal microflora are recommended. To eliminate toxins should drink plenty of water, fresh juice, green tea and oolong tea.
Additionally, you can use folk remedies to help improve the condition of the patient:
- It helps to remove toxins from white pharmacy clay, which you need to drink for six months as a drink: 1 tsp in a glass of water, put it overnight, and in the morning stir and drink on an empty stomach.
- For cleansing the blood and lymph helps algae powder: 1 packet for 10 days in the evening, a break of 10 days and repeat up to 5 months.
- Vegetable decoctions and infusions of nettle, horsetail, wormwood, immortelle, borage, calendula, linden flowers, mountain ash, dog rose are prepared from 1 tbsp of grass per 0.5 liter of boiling water, drink for 15 minutes. before meals, 250 ml. Long-term treatment, alternating plant species monthly for several years;
- For the treatment of erythema it is recommended to make compresses with herbs.
- Lubricate the tick bite with the juice of celandine, plantain, walnut oil.
Important!
Throughout the course of treatment for Lyme disease, alcohol, coffee, sweet foods, nutritional supplements are contraindicated due to a strong increase in the load on the liver and provoking the growth of bacteria.
Lyme disease prevention
The only preventive measures are methods of preventing ticks from falling on the human body. When visiting the forest, going on a picnic or nature, it is recommended to wear maximum closed clothes, use repellents to scare off parasites.
If a tick that has adhered to the skin is detected, it is recommended, after removal, to place it in a glass container. Then take it to the laboratory, where you can do a tick analysis for borreliosis to determine the likelihood of a person becoming infected.
If an infection is suspected, antibiotic therapy with 2 drugs is recommended for prophylaxis:
- Doxycycline - take 100 mg daily for 5 days;
- Ceftriaxone - 100 mg 1 p. per day 3 days.
Taking such drugs, as indicated by reviews of patients with Borreliosis, will help prevent Lyme disease in 80-95% of cases after being bitten by an infected tick.