Tick bite diseases in humans
Content
- Tick Disease
- Diseases caused by tick bites
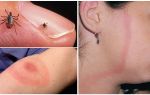
A common summer disaster - a tick, not only creates inconvenience for walks into the forest and the river, but can bring much more serious problems. In addition to the frightening of all tick-borne encephalitis and borreliosis, there is still a list of diseases carried by ticks.
What diseases do ticks suffer?
All tick-borne infections are obligate-transmissible diseases.That is, diseases that can be transmitted from animal to human.
Tick-borne infections include:
- encephalitis;
- borreliosis;
- tularemia;
- typhus;
- spotted fever;
- Qu fever;
- hemorrhagic fever;
- anaplasmosis;
- ehrlichiosis;
- babesiosis.
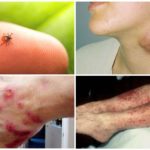
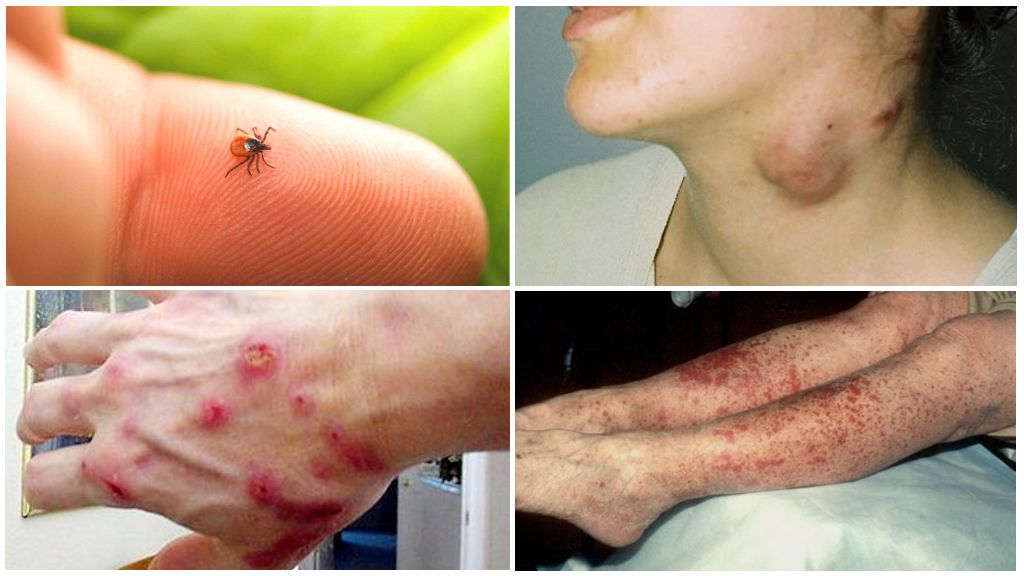
These diseases from ticks in humans occur after a bite of an arthropod. But the disease itself will not occur from the bite. It is necessary that the aggressor was the carrier of the pathogen. In areas that are prosperous due to the epidemiological situation, the probability of being infected with something unpleasant after a tick bite is small. If there is an epidemiological hazard in the area, then the risk of meeting with an infected tick is very high. In the taiga regions, unfavorable for encephalitis, every fifth tick is a distributor of this disease.
Important!
There is a very dangerous misconception that the probability of illness as a result of a tick bite is less, the faster the parasite has been removed from the body. In fact, the probability of infection is far from zero even in the first moments after a skin puncture. The tick itself does not set the timer either. Since there is no pain at the tick bite, it is impossible to say how long the bloodsucker spent, feeding on blood.
To reduce the likelihood of illness after a tick bite, you must use preventive measures and know the symptoms of the onset of the disease.
Encephalitis
It is believed that this disease suffers only "special" encephalitis tick. Not. This disease transmits any blood-sucking parasite. So, any kind of Ixodes ticks, which can be found in the forest and on the meadows.
Encephalitis tick infects a person at the time of the bite. The first few days the incubation period lasts, and the person feels healthy. Then, depending on the type of encephalitis, symptoms appear that are similar to other, less dangerous diseases.
Symptoms of European tick-borne encephalitis:
- first stage: muscular and headache, nausea and vomiting, anorexia, fever;
- remission;
- second stage: damage to the central nervous system with the development of meningitis or encephalitis.
On a note!
Far Eastern encephalitis is much more severe: temperature 38-39 ° C, nausea, severe headache, sleep disturbance, after 3-5 days - damage to the central nervous system.
Given the danger of the disease, many are interested in the question of whether tick-borne encephalitis is transmitted from person to person. With simple patient care not. For this you need a vector.But to find an infected tick that, at the larval or nymph stage, drank the blood of a person with encephalitis and “plant” it on himself, can only be done consciously. Such an event requires a long preparation. Simply walk in the woods.
Borreliosis, he's Lyme disease
The most common tick-borne disease in Europe and the United States. The incubation period from tick infestation to the first signs of 1-2 weeks. The cause of infection is not imago, but nymphs, so the peak of the incidence of borreliosis occurs in May-September. The disease is caused by a whole group of bacteria of the genus Borrelia.
Borreliosis has three stages:
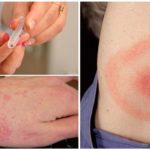
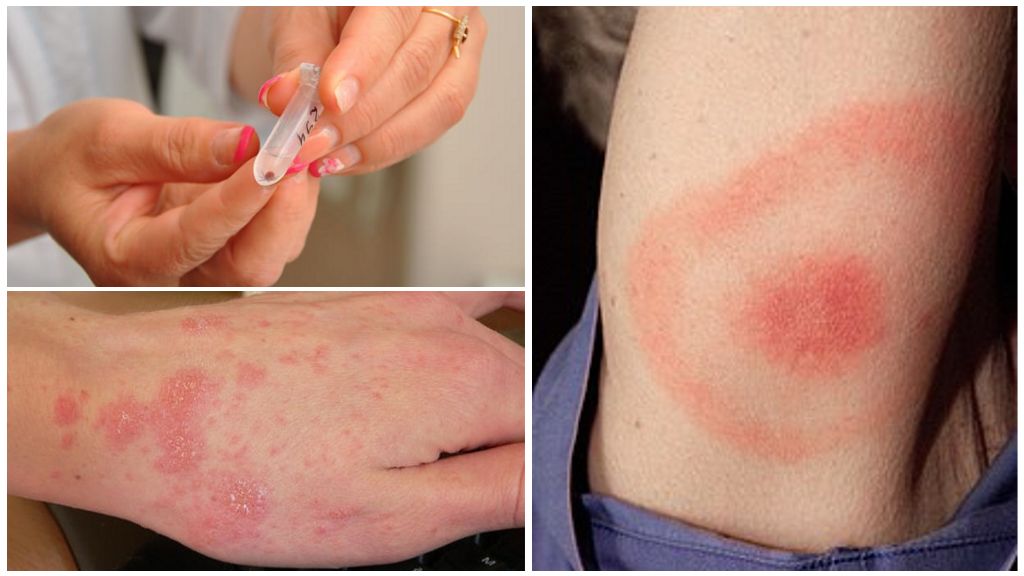
- First: common symptoms: headache and muscle pain; temperature 38 ° C; chills, vomiting, nausea; possible pain and sore throat, cough. Local symptoms: the bite reddens, swells, itching and soreness, ring-shaped erythema.
- The second: damage to the central nervous system; all signs of the first stage disappear.
- Third: develops after a few months / years, Borelia are spread throughout the body and can settle in any organ. Cause damage to the central nervous system, arthritis, acrodermatitis.
The disease usually “chooses” the weakest system of the human body and starts its activity from there. Later damage to other organs or systems is possible.
Important!
Borreliosis is curable, but treatment is necessary under the supervision of doctors. Best of all, the disease is cured in the first stage. But even a third person can be helped.
Ehrlichiosis
Anaplasmosis and Ehrlichiosis are caused by related bacteria. Frequent cases of ehrlichiosis occur in the United States, where there is a natural focus. Since the causative agents of babesiosis and borreliosis are also present, complex infection with viruses from the same arthropod can occur.
The symptoms of these two diseases are similar. About 12 days after the tick attack, the person feels:
- weakness;
- myalgia;
- nausea;
- chills;
- headache.
A person also begins vomiting, coughing and fever.
Babesiosis (piroplasmosis)
A man was first diagnosed in 1957 in Yugoslavia, but today it is already distributed throughout Eurasia.
Babesiosis belongs to vector-borne diseases and in humans it is poorly differentiated from other infections. The incubation period lasts 3-21 days.In the first 10 days of the acute course, a person feels weak, headache, prostration. Nausea and vomiting occur. On the 3-4th day jaundice begins to develop, the liver increases. After 6-7 days, oligoanuria and hemoglobinuria develop. Further, a person develops acute renal failure. Without treatment, the disease ends in death.
On a note!
The causative agent of babesiosis persists in the body of arthropods for life.
Identification of an infected tick
Such a procedure can be carried out only in the laboratory at the clinic or hospital. It is impossible to determine the carrier of infectious diseases by eye. You can only focus on the general situation with tick-borne infections in the area. Viruses of dangerous diseases carry all Ixodes mites and a significant part of argasaceae. We are all used to being afraid of the taiga “red” tick, but the spotted tick, the inhabitant of grass meadows, may also be the carrier of encephalitis. And not only encephalitis.
But doubts whether or not all ticks are contagious have a basis. Any type of ixodic can be carriers, but not every specific individual will necessarily transmit the disease.Since it is impossible to distinguish an infected tick from an uninfected one without special studies, it is necessary, by default, to consider all arthropods as carriers of any disease.