Symptoms and treatment of piroplasmosis in dogs
Content
- Piroplasmosis in dogs
- Drugs for piroplasmosis in dogs
- Treatment of dogs for piroplasmosis
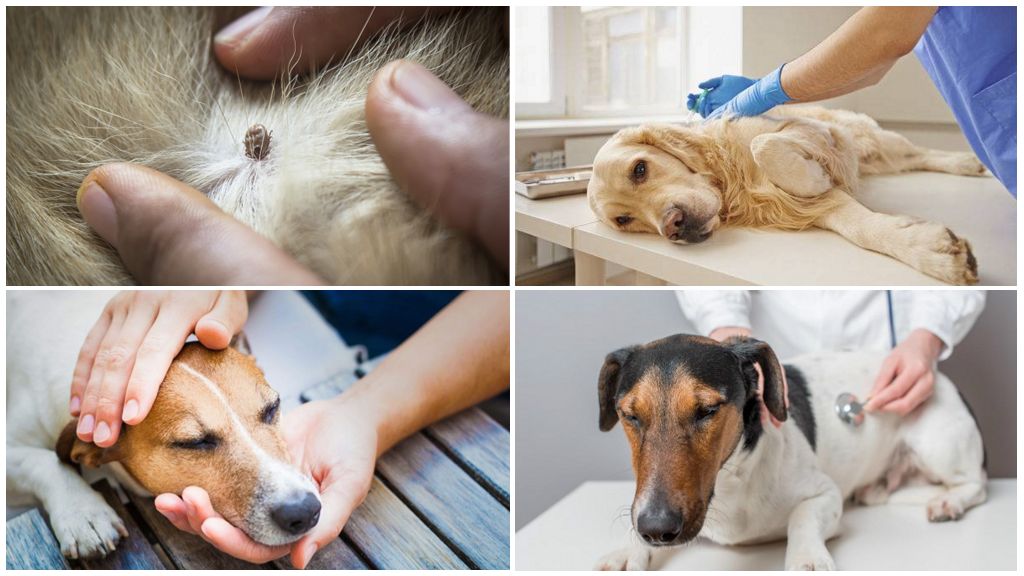
Piroplasmosis in dogs or babesiosis is a dangerous disease, spread by ticks. The incubation period lasts from 3 to 14 days. It is manifested by a sharp deterioration in the well-being of the animal, or it proceeds without pronounced symptomatology. Therapy is carried out with the help of special drugs under the supervision of specialists.
Animal infection
The pyroplasmosis mite lives everywhere. Prefers broadleaf plants, shrubs, tall grass, thickets. It feeds on the blood of wild animals, birds, pets, livestock. Infection of domestic dogs occurs during a walk near the house, in the forest, on the lawn.
A tick transmits an infection during a bite through saliva. The first signs of piroplasmosis in dogs appear a few days after the parasite, full, disappears. How long the incubation period lasts depends on the immune system of the animal. Puppies, young dogs under the age of 3 years, purebred dogs react acutely to infection. The first signs may occur 2-14 days after the tick bite.
On a note!
The first outbreak of babesiosis is observed in early spring, when ticks are activated, a young generation of pests appears. During the entire warm period, dogs are at high risk of infection. In the wild, mites can bite wolves, foxes, jackals.
Biology of the pathogen
Piroplasmosis is provoked by babesia, which replace the two masters for the entire cycle of their development. The first are ticks.Infection occurs when a sick animal bites. Dogs also become infected after eating the sick parasite.
Babesia enter the bloodstream, begin to actively share. Unicellular microorganisms develop in red blood cells, feed on hemoglobin. After some time they begin to transform, falling into the stomach.
On a note!
In ticks, parasites are found in large numbers in saliva, therefore, when they are bitten, they enter the blood mass. Babesiosis in dogs develops rapidly, the clinical picture directly depends on the body's defenses.
Symptoms and treatment of piroplasmosis in dogs
In most cases, the first signs of infection are pronounced, literally knocking the pet down.
Acute disease
In the first days, body temperature rises to 41 degrees Celsius. In pets with a strong immunity or animals that have already been ill with piroplasmosis once, the heat lasts 1-2 days. In other cases - up to 3.
In the process of vital activity of microorganisms, toxins are released, which are carried by blood throughout the body. Lowering hemoglobin significantly weakens the vitality of the dog.As a result, characteristic symptoms of piroplasmosis appear.
How the disease manifests itself:
- vomiting;
- lack of appetite;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- apathy;
- nausea;
- insomnia or drowsiness;
- the mucous membranes of the eyes and mouth are pale;
- urine becomes darker;
- weakness of the hind limbs;
- feces of yellow, green tint;
- pulmonary edema.
On a note!
In the absence of proper measures, the dog may die within 5 days or the immunity will develop antibodies, the disease will defeat itself, will make the pet more resistant to babesiosis. However, no bona fide owner will check. The latter situation is characteristic of homeless, yard dogs.
Sluggish course of the disease
For piroplasmosis also characterized by a sluggish course with a weak clinical picture. This situation happens with strong immunity in animals when the body itself is trying to cope with pathogens. The dog may look just tired.
The owner may note a slight deterioration in the well-being of the pet, which is expressed in weakness, apathy, lack of appetite, a violation of the chair. The temperature rises to 42 degrees Celsius for just one day or stays within the normal range. A weak onset is a dangerously long recovery period.
On a note!
Chronic piroplasmosis is also observed in pets that had previously been ill with this ailment, antibodies developed. In this case, the illness lasts up to 90 days.
Diagnostics
Treatment of piroplasmosis in a dog after a tick bite begins with a visit to the veterinarian. To determine the disease, the animal takes blood, urine. The obtained data analysis is compared with the clinical manifestations, appropriate drug treatment is prescribed. In severe cases, blood transfusions are performed in dogs with piroplasmosis.
Effective drugs
Without qualified therapy, the mortality rate is 98%. At the first manifestations of the disease, it is necessary to seek help from doctors, to be examined. Treatment is carried out in several directions.
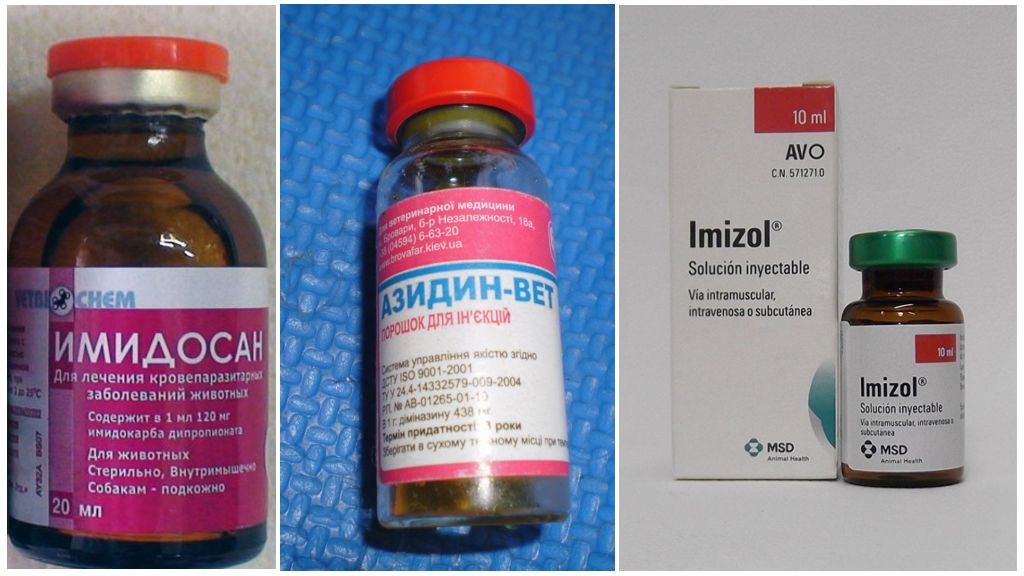
The first stage is the use of drugs to destroy parasites affected by red blood cells. Preparations for the treatment of piroplasmosis in dogs:
- Imidosan;
- Veriben;
- Azidine;
- Imizol;
- Doxycycline;
- Berenil;
- Imidocarb;
- Fortikarb.
The veterinarian can treat or inject vaccine independently.
The following steps are aimed at eliminating the waste products of pathological microorganisms, restoring the normal functioning of the digestive system.Assign pills to normalize the health of the dog, enhance the protective functions, strengthen the immune system. Hepatoprotectors, vitamins, medicines for heart maintenance are prescribed.
Forced alkalizing diuresis is prescribed to prevent complications, to eliminate them. After the injection of antiparasitic drugs is introduced, a massive death of pathogens occurs. Toxicosis appears, a significant deterioration in the state of health of the animal. The remains of cells are excreted through the kidneys, their blockage occurs. In order to eliminate renal failure prescribe forced alkalizing diuresis.
A new method of treatment of piroplasmosis, aimed at the purification of blood plasma - hemosorption, plasma exchange. It has been used in veterinary practice since 2007. Assign with the purpose of removing toxins, cell residues after mandatory medication, as well as from the first days after the diagnosis is confirmed. The main advantage of the method is that blood purification occurs without the participation of the kidneys, liver, which reduces the risk of severe side effects.
The duration of therapy and the success of treatment depends on the complexity, features of the disease, period. With timely assistance, the dog recovers within 8 days. With late treatment or in the presence of complications - 20 days.
Important!
There is a special vaccine against piroplasmosis in dogs that protects the animal from a fatal disease. Preparations are called Pirodog, Nobivak Piro. Contained isolated antigen, which reduces the risk of death, but does not provide 100% protection. For the prevention of piroplasmosis, standard means from blood-sucking insects are used.
Possible complications
Effects:
- lung enlargement;
- liver damage;
- ischemic brain damage;
- renal, heart failure.
Convulsions are rare, ending in the death of an animal. Renal failure is a frequent occurrence, but if urine is formed, there are chances to save the pet.
Complications include the chronic course of piroplasmosis. After the disappearance of the bright, painful, unpleasant symptoms, there is no complete recovery, the parasites are present in the blood, gradually poisoning the pet's body.When the next bite infected tick aggravation occurs.
Important!
In severe situations in the blood of dogs there are several types of babeziy, which gives a complication to many internal organs and systems. To cure an animal is very difficult, expensive. There are also situations when a pet is sick, but it is impossible to establish a diagnosis by analysis.
Preventive measures
With the onset of heat at home, the dog is treated with any modern means for blood-sucking parasites. Apply drops, spray, lotion, cling special collar. No remedy provides 100% protection, but reduces the risk of disease at times. Spray, drops, lotions act on ticks for about 2 weeks, collars depending on the active component - from 1 month to 3.
Additionally, folk remedies are used in the form of decoctions of wormwood tansy, solutions with the addition of lavender essential oil, citronella, lemongrass. Spray wool from a spray or put drops.
Whether to do vaccination against piroplasmosis, each owner decides on his own. But he must do everything to save the animal from a dangerous disease.