What is encephalitis tick, its photo and description
Content
- Tick-borne Encephalitis
- Dog tick
- Taiga tick
- Tick life cycle
- Pliers
- Symptoms of European encephalitis in the first stage of the disease
Encephalitis is one of the most dangerous viral diseases, incurable so far. The vector of encephalitis can be any “reusable” bloodsucker, first drinking blood from an infected animal, and then “snacking” by humans.But the main danger is ticks, popularly called encephalitis. Separate species "encephalitis tick" in nature does not exist. The main carriers of this disease among arachna-like are two types of ixodus ticks at once: the dog and taiga.
The spread of encephalitis virus
Ticks are found throughout the Eurasian continent, but the risk of becoming infected with encephalitis is only in the inhabitants of a rather narrow strip, which passes approximately in the middle of Eurasia.
On a note!
In Russia, there are all three types of encephalitis virus. In the European part, the spread of the disease is the dog tick, in the Asian part the taiga tick.
There is a clear division of territory between types of viruses: a virus of the European type is present on the territory of the Russian Federation, after the Ural Mountains across Siberia to the Far East, the Far Eastern type of encephalitis is raging. The natural reservoir of the virus - sick animals whose blood feeds on these arthropods.
Tick infestation by encephalitis is also higher in the Asian part of Russia. Beyond the Ural Mountains, 20 percent of ticks are infected with a virus.
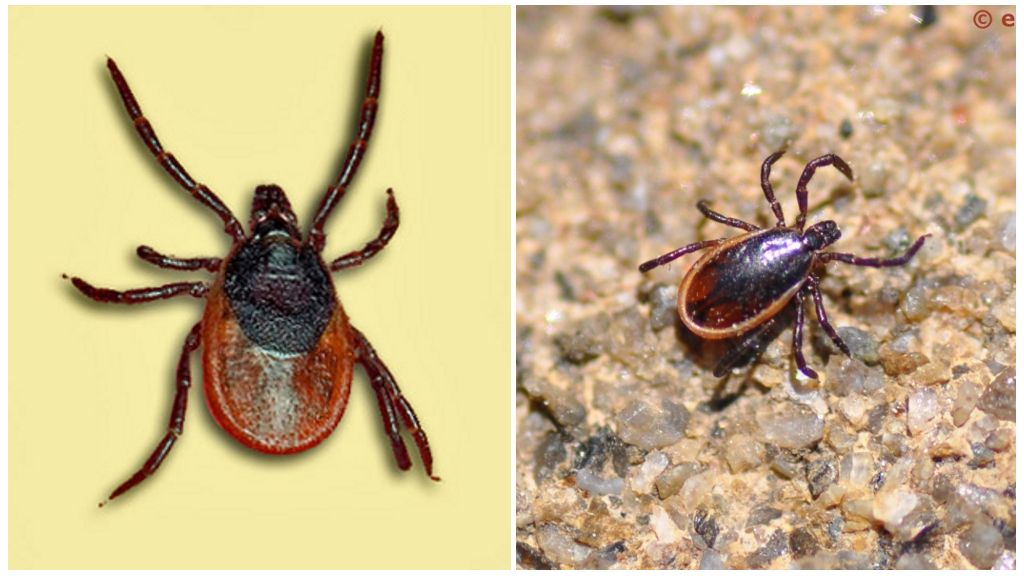
What does an encephalitis tick look like?
Since there is no separate arachnoid-like virus that carries the virus, there is also no photo encephalitis tick. But, in order not to clarify each time the type of tick, it is easier to call encephalitis an arthropod that is infected with a virus and can transmit diseases to humans. Also need to consider the species that most often transmit the virus to humans. In all other cases, the risk of getting an infection is not higher than when eating raw milk.
Dog tick
The Latin name of the species is Ixodes ricinus. Arthropods are widely distributed throughout the Eurasian continent. You can also meet him in North America and North Africa. There is no encephalitis virus on the last two continents and this type of tick is not exactly encephalitic. But it can reward other dangerous diseases.
Canine mite - an ordinary, familiar to almost all arachnopodobnoe. Dog owners are more worried about piroplasmosis spread by them than encephalitis virus. The sizes of arthropods can be different depending on what stage of development the tick decided to drink blood. Larvae and nymphs begin to drink blood, differing only from imago in size.A hungry nymph has a length of 1.3-1.5 mm. Adult male - 2.5 mm. Hungry adult female 4 mm long. After she is full, she swells to 1.1 cm.
The body of the dog tick has the shape of an egg with a very sharp tip; there is a proboscis on the head. The back is protected by a shield of dark brown color. The males completely cover the entire body. In females, larvae and nymphs, the shield is much smaller and protects only the front part of the back. The belly of a hungry female is gray below and black above.
On a note!
After saturation, the abdomen swells up, and the tick begins to resemble a small gray bag of leather with legs on the front side.
Taiga tick
The second representative of Ixodes with the Latin name Ixodes persulcatus. The main range of this species is located in the middle and southern taiga. Taiga is associated with Siberia, so sometimes there is another name for this species: Siberian tick.
The boundaries of the present range of this tick:
- West: Leningrad, Moscow regions;
- east: down to the Pacific;
- north: South Karelia;
- South: Samara and Ulyanovsk regions.
Outside Russia, the tick range captures Finland, the Baltic States, Belarus, and northwestern Europe. Separate foci are found on Kamchatka and the Kuril ridge.You can meet him in the mountainous regions of Central Asia.
Important!
In the Crimean forests there is a mite that looks very similar to the taiga. The peculiarity of the “Crimean” tick is the ability to bite into the skin to half of its body. Taiga feeds similarly. It is possible that this one and the same view.
The entaphalitic tick is most often identified as taiga due to the fact that in a large part of its area this disease is very common.
Important!
Recently, this species is increasingly found in cities.
The size and shape of the body of an “encephalitic” tick are similar to its relative - the dog. But the belly of a hungry taiga tick is red.
Blood-sucking they become already at the stage of the larva. If a nymph differs from imago only in size, then the larva is a small translucent organism, already at this stage capable of transmitting the causative agent of the disease.
Important!
The female is able to transmit the virus to offspring, and the new generation is born already infected. Therefore, it is impossible to determine by the appearance of an arthropod that it is a carrier of a viral disease. Even the larva can be a carrier of the virus.
Lifestyle
The European part of Russia is relatively safe for encephalitis, while in Siberia, outbreaks of the disease are observed in early spring, when there are no other blood-sucking parasites yet.
There are allegations that an adult individual lives only for 3-4 months, but the appearance of the disease in early spring is due to the fact that already at a temperature of 1 ° C encephalitis ticks wake up after wintering and go in search of the victim.
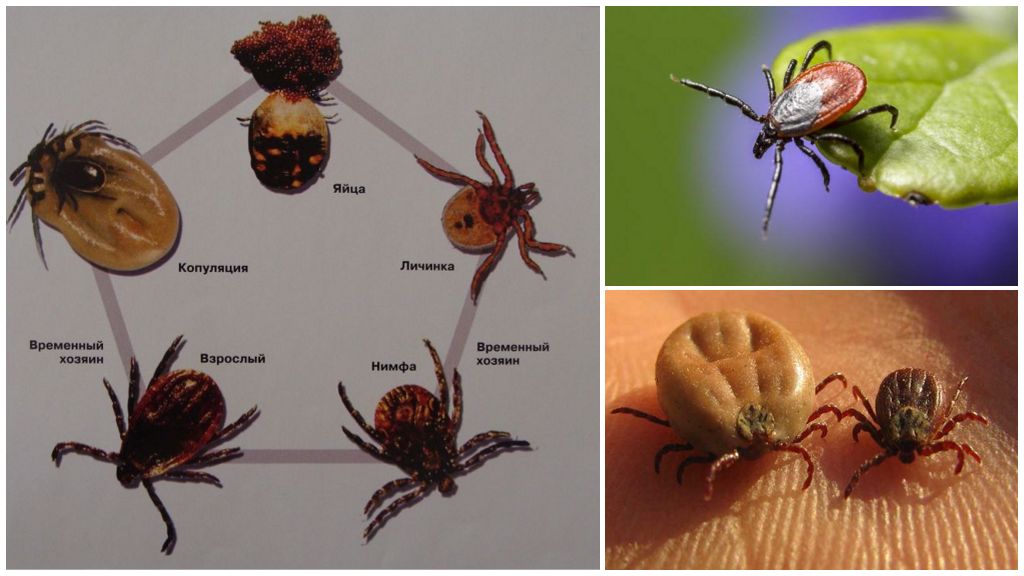
In fact, the life cycle of an encephalitic tick can be from 2 to 4 years. The life span of an arthropod depends on environmental conditions. The minimum development cycle takes 2 years, in the northern regions, the development time from egg to imago can be 4 years. The average development period is 3 years. With a three-year period, the development of each stage of an encephalitic tick takes 1 year. In winter, diapause occurs in arthropods.
At all stages of development, encephalitis mites overwinter in forest litter, stone cracks, in the surface layer of the soil. Both the hungry and the drunk blood of the individual go for wintering.
The preimaginal stage takes 2–20 weeks. Its duration depends on environmental conditions.The maximum activity of sexually mature encephalitic ticks occurs in May-June. Larvae come out of eggs in the middle of summer.
On a note!
Adults can survive without food for up to 3 years. The female should leave offspring, and she can wait for a suitable opportunity for a long time. As a result, it turns out that the answer to the question of how long an encephalitis tick lives is very vague. Under adverse conditions and lack of food, the life span can last up to 6 years. Or shrink to 2, if the conditions for the life of arthropods are favorable and a quick turn of generations is needed.
Blood parasites are needed not only for their own development, but also for the laying of eggs. Therefore, the males eat little blood, sometimes doing completely without it. Females drink a lot. The female, which was sucked in without being disturbed, impresses with its large size.
Tick infection
Encephalitis mites feed on the blood of any mammals, as well as birds. In the area of the disease, arthropods' hunting objects are often infected with encephalitis virus. When feeding the victim with blood, the tick "drinks" and the virus. This is the main variant of how ticks become infected with encephalitis. The second way is the transmission of the virus from the female to the offspring.
The fact that they have an encephalitic virus is indifferent to the arachnoid-like virus, so there is no way to recognize “by eye” in the field conditions of an infected bloodsucker.
On a note!
Find out: encephalitis tick or not, you can only passing it to the laboratory.
Precautionary measures
Ixodes are waiting for their victims, sitting on grass stalks and branches of bushes. They rarely rise above a meter above the ground. There is no way how to detect an encephalitic tick right in the forest, so you need to take precautions when using protective clothing.
In contact with the victim, the arthropod starts upward. This point is taken into account when collecting in the forest. Pants tucked into socks, sweater into pants. The sleeves of a sweater or jacket are cuffed. On halts conduct a thorough inspection of each other. Ticks that have not had time to dig in remain on clothes, from where they can be easily assembled.
When returning from a hike, they take off all their clothes and carefully inspect the body. If arachnid managed to get under his clothes, then he can cling anywhere.
Important!
The tick bite is painless, although it causes a local allergic reaction.
It is only possible to distinguish an encephalitic tick from a normal non-infectious after laboratory research. Hence the recommendations: carefully remove the bored bloodsucker and take it to the laboratory. It is especially important to comply with this condition in areas unfavorable for encephalitis.
The bite of an encephalitic tick is dangerous, even if the arthropod has spent very little time on the victim. For infection with viral encephalitis, it is enough that the parasite only pierced the skin and managed to inject its saliva there.
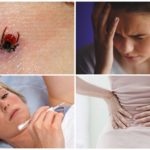
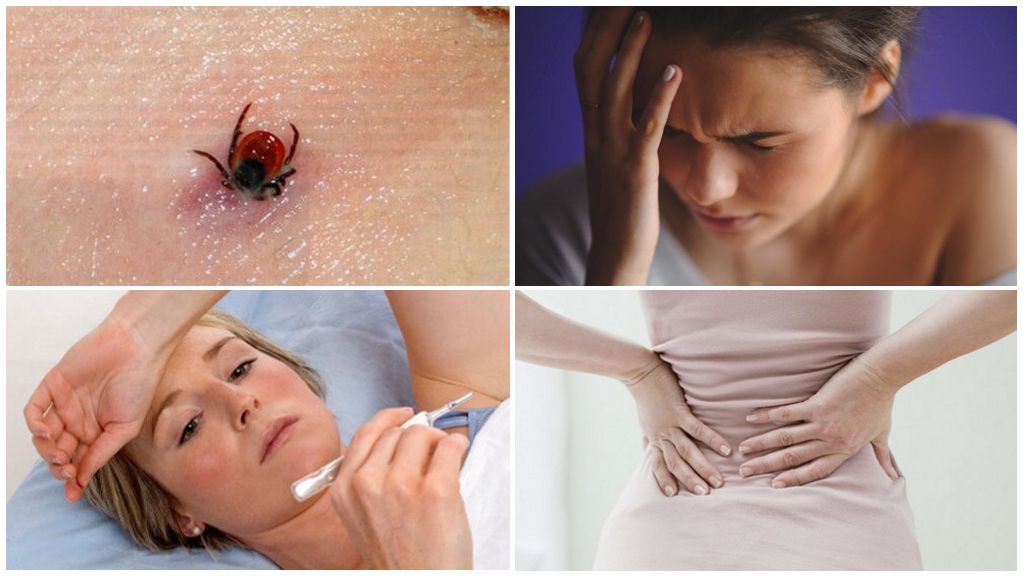
Symptoms of the disease
Irritation at the site of the bite quickly passes, and the person forgets about the incident. But after 1-2 weeks he feels unwell and does not associate it with the arthropod that bit him.
In the first stage, it is very difficult to distinguish between encephalitis infection and other diseases, of which there are a good dozen. And not all of them are contagious.
The main symptoms of European encephalitis in the first stage, lasting 2-4 days:
- muscle pain;
- lack of appetite;
- headache;
- fever;
- nausea, possibly with vomiting;
- general malaise.
At this stage, encephalitis is easily confused even with ordinary flu and try to self-medicate. After 8 days (the period of complete recovery from the flu), remission occurs.The patient sincerely believes that it was the flu and forgets about the disease. If you are lucky, there will be no consequences.
But in 20–30% of those infected, after remission, the second stage of the disease with CNS damage follows:
- meningitis: severe headaches, tense muscles of the neck (similar to myositis), fever;
- encephalitis: impaired coordination of movements up to paralysis, disorder of sensitivity, impairment of consciousness;
- mixed form, which "will please" simultaneous signs of encephalitis and meningitis.
Far Eastern encephalitis develops more rapidly. It begins with a sudden increase in body temperature to 38–39 ° C. There is a severe headache and nausea. Sleep is disturbed. There is no remission. After 3-5 days, a CNS lesion develops.
Important!
Mortality in Far Eastern encephalitis is higher than in European. Drug treatment of the disease is not developed.
No matter what color the tick had time to dig into the body. In terms of transmission of infection between them there is no difference. Moreover, in a contaminated area, any blood-sucking organism parasitizing mammals can be dangerous. To prevent infection, you must comply with safety measures and take care in advance of encephalitis vaccination.