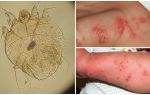
Description and photo of moose mite
Content
- Elk mite
- Elk mite breeding
- Deer bloodsucker
What troubles just do not lie in wait for a man in the forest. And they can be not only wild animals, but also various insects. Find in the tangled hair of the head of the flies have been seen by many. A little later, small papules form on the human body, accompanied by itching, redness and pain. All these symptoms are evidence of the attack of the deer bloodsucker, which is popularly referred to as the moose mite.
What it looks like
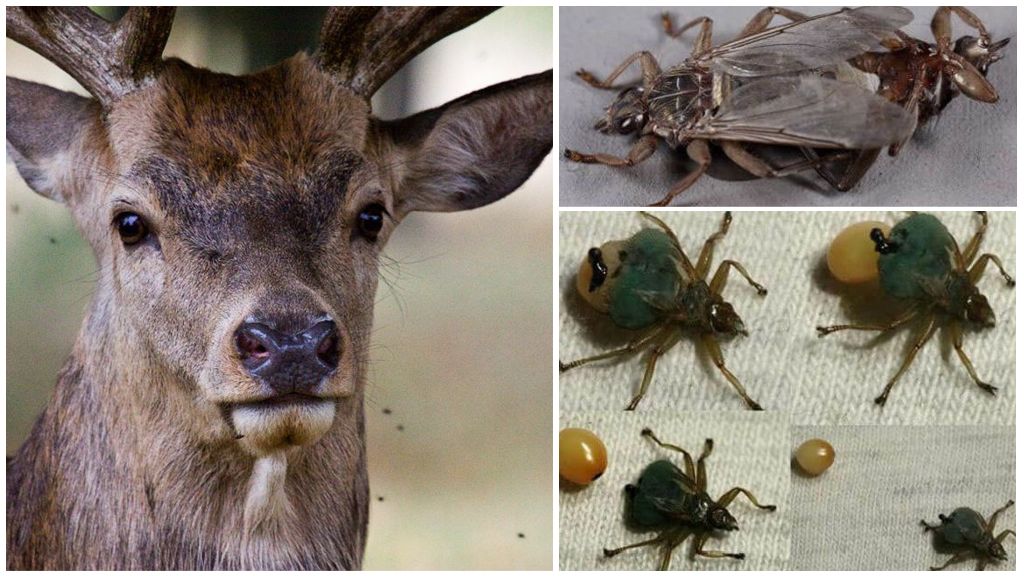
The bloodsucker deer, elk mite, deer louse, or elk flea are all names for one parasite that lives on elk, deer, and other members of the family of hoof grabs. Boars and foxes, bears and badgers, goats, sheep and cattle can also be subject to blood sucking attacks.
On a note!
Quite often, an ectoparasite is confused with a tick, since, having attacked the body of the victim, the pest breaks off its wings and fastens its legs by the hair. However, this statement is not true: the bloodsucker doesn’t belong to mites. The blood-sucking parasite of warm-blooded Lipopténa cérvi is one of the species of the bloodsucker of the family Hippoboscidae Samouelle.
What it looks like:
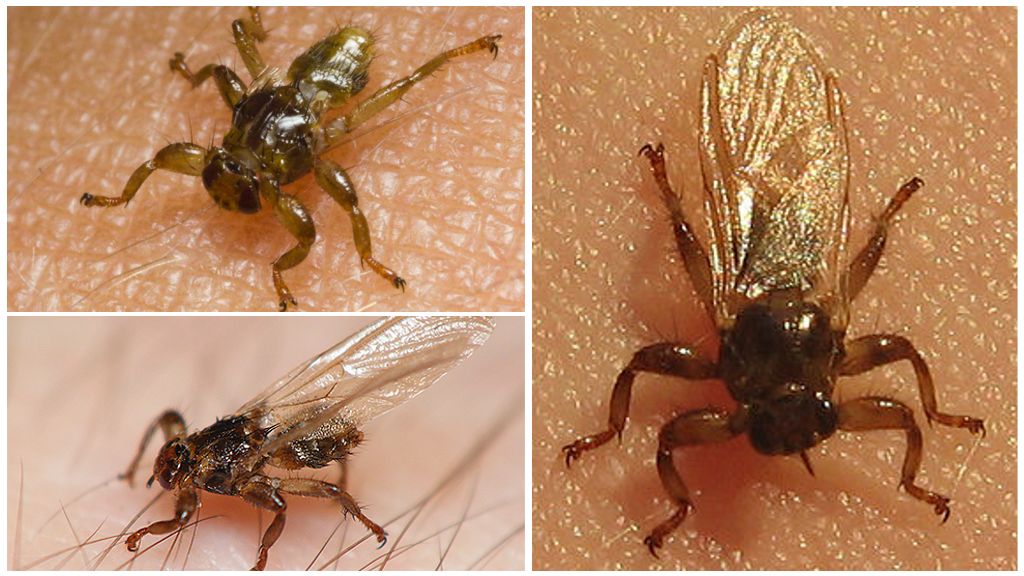
- Externally, moose mite is similar to a small fly, whose body size does not exceed 3.5 mm. Moreover, females are usually larger than males (a photo of an elk tick is presented below).
- The light brown color of the fly has a soft and elastic abdomen, which is able to stretch when taking a large amount of food and carrying offspring.
- The blood sucker is the owner of 3 pairs of strong legs growing from the breast, at the ends of which there are asymmetrical claws.
- The antennae and rather large eyes of the facet structure are located on the flattened and directed head of the moose mite, in addition to them there are also 3 simple ocelli.However, the bloodsucker does not shine with his eyesight, focusing on the terrain and the victim on the contours.
- On the sides of the dense leathery body of a deer bloodsucker are well-developed transparent wings. But flying pest is not very good and can not fly over long distances.
A tick-like fly has a piercing-sucking type oral apparatus, which is similar in structure to the scapula, which makes it easy to pierce the skin of an animal or person. A more detailed look at the structure of the ectoparasite can be on the photo of the deer tick presented below.
Where dwells
Elk mites are common in northern China, Scandinavia, and North America. You can meet flying bloodsuckers in Russia, especially in the European part of the country and in Siberia. The number of pests varies depending on the number of deer artiodactyls.
Dwells bloodsucker in the forest, being on the bushes and trees in anticipation of a suitable victim. The ectoparasite prefers to live in the thick hair of animals, since it is convenient to cling to the hairs with claws. Due to the fact that this can not be done on the skin of a person, a bloodsucker when attacking people is limited to bites only.
Interesting!
A single dose of blood consumed by a parasite can reach 1.5 ml, and the number of pest meals per day is up to 20 times.
About nutrition and reproduction
Like its other relatives of the family Hippoboscidae, elk flea has a live birth, and therefore, the development of eggs and larvae continues in its womb. Usually this process occurs at the end of September. After 2-3 days, very large sizes (up to 4 mm) of prepupae or puparia, which the female gives birth at certain time intervals, are born. After 2 days from the time the uterus is emptied, the next larva enters it from the uterus-like expansion of the oviduct, which is born in a similar way. During life, the female gives birth to about 20-30 puparia.
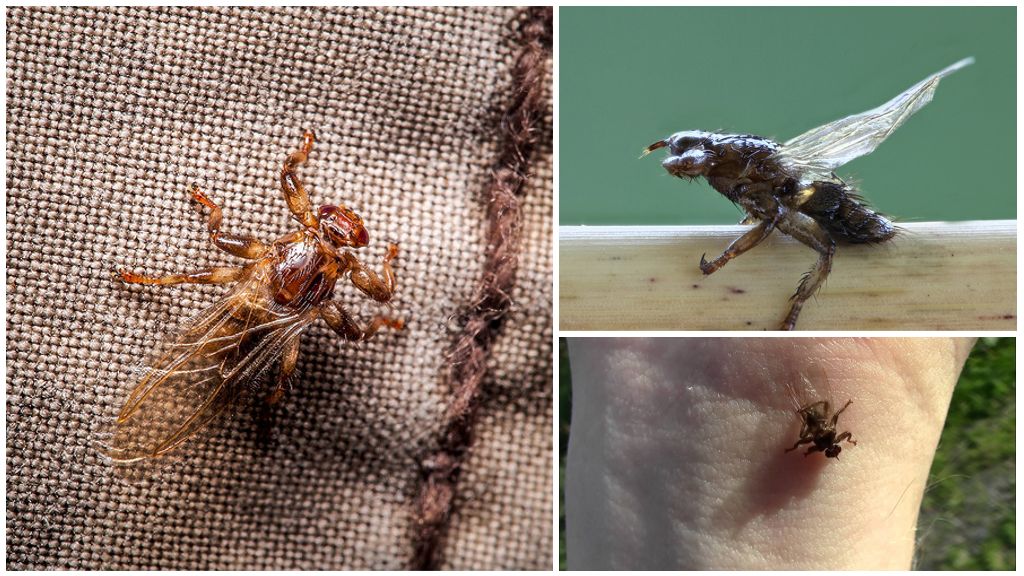
The body of the puparia is not growing, but only acquires a dark color and a hard surface. Then it falls to the ground, where it remains to winter. The development of the future individual will continue only with the arrival of spring. The process of pupa formation takes up almost the entire summer period up to August, as a result of which an elk mite with wings appears (the photo of the flying mite is presented below).In some areas of the Russian Federation, the appearance of adult individuals is delayed until mid-October.
The newly-minted individual settles on a tree or shrub, where it lurks its prey. When such a bloodsucker is detected, it clings to the animal's hair, drops its wings, and, upon reaching the skin, proceeds to a meal. After 15–20 days of active feeding, flies begin to show sexual dimorphism: their body darkens, their head decreases, their abdomen grows and their wing muscles atrophy. After that, mating of adult individuals occurs: having chosen a female partner, the male tightly clings to her, continuing to live as a pair afterwards.
On a note!
From the moment of departure of the winged individual, it takes about a month, after which the process of puparia appearance resumes. The wingless parasite lives on the body of the host for up to 6 months, so the artiodactyls can get rid of the bloodsuckers only by the beginning of summer.
Is elk mite dangerous for humans?
Not only animals are subject to blood sucking attacks, man can also become a victim of a pest. The reaction to an elk flea bite varies: some do not feel the injection at all, others may experience pain and sometimes very severe.And more often such a reaction is observed in people with sensitive skin.
After 1-2 days from the moment the bite is inflicted by the parasite, a slight condensation and redness appear in the lesion focus area, and itching is felt. It is also possible manifestations of an allergic reaction, as a result of which there are long blistering and covered with a dense crust of eczema.
On a note!
As a result of long-term observations, the specialists managed to find out that during the primary attack of the parasite, the human immune system is much more active in resisting the invasion of toxins. For people who had been attacked by bloodsuckers for several years, the effects of bites were more severe. As a result of numerous studies, scientists have observed that at least 20% of elk mites contained spirochetes (Lyme disease causative agents).
Therefore, to prevent an elk tick attack, it is necessary to choose the right equipment. Maximum closed clothing should be spacious enough to have a tight-fitting cuff and hood. And the edges of the pants must be refilled in socks or shoes. For the protection of the face and neck, use a mosquito net.Reliable protection against insects can also be made by repellents, in which DETA acts as an active substance.