What does the Colorado beetle look like? Photo and lifestyle
Content
- Colorado beetle
- Colorado potato beetle larva
- Life cycle of the colorado potato beetle
- Colorado potato beetle eggs
- False Colorado potato beetle
Colorado beetle on hearing almost every person. Many encounter him in their personal plots and try to immediately get rid of this pest before it has destroyed the entire crop.It belongs to the family of leaf beetles, detachment - beetles. Scientists do not isolate species of this pest. It is desirable to know the enemy in person, so it is interesting to get information about how the Colorado potato beetle looks, what it feeds on, its life cycle, whether it flies or not, how it differs from its counterparts, from where it came from.
A bit of history, the origin of the name
Those who are interested in the question of whether the Colorado potato beetle is an insect or not can be safely answered - yes, it is an insect. Mexico is his homeland. For the first time, people encountered him in 1824, when they saw that an unremarkable beetle eats leaves of tomato, tobacco, and other crops. When they began to cultivate potatoes in America (Colorado), he decided to try its leaves too. They liked him very much and since then they have become the main delicacy for the beetle in spring and summer.
Interesting!
At the end of the fifties of the last century in the USA, the insect Colorado potato beetle, along with its tribesmen, caused enormous damage to potato fields. In this country, the name “Colorado potato beetle” stuck with it.
Since then, this pest began to gain more and more territory for itself, mastering new places. In the Soviet Union, it was discovered in Ukraine after the end of the war in 1949.After 4 years, entire clusters of pests were recorded in Russian cities - Brest, Kaliningrad, Volyn and other areas. The warm weather gave them the opportunity to move to the cities of Belarus, the Baltic States, they began to live throughout Ukraine. Every year the population of the Colorado potato beetle increased, and today it can be found almost throughout the entire territory of Russia.
What does a beetle look like
The Colorado potato beetle is a frequent visitor in the fields and gardens, so many have seen it more than once.
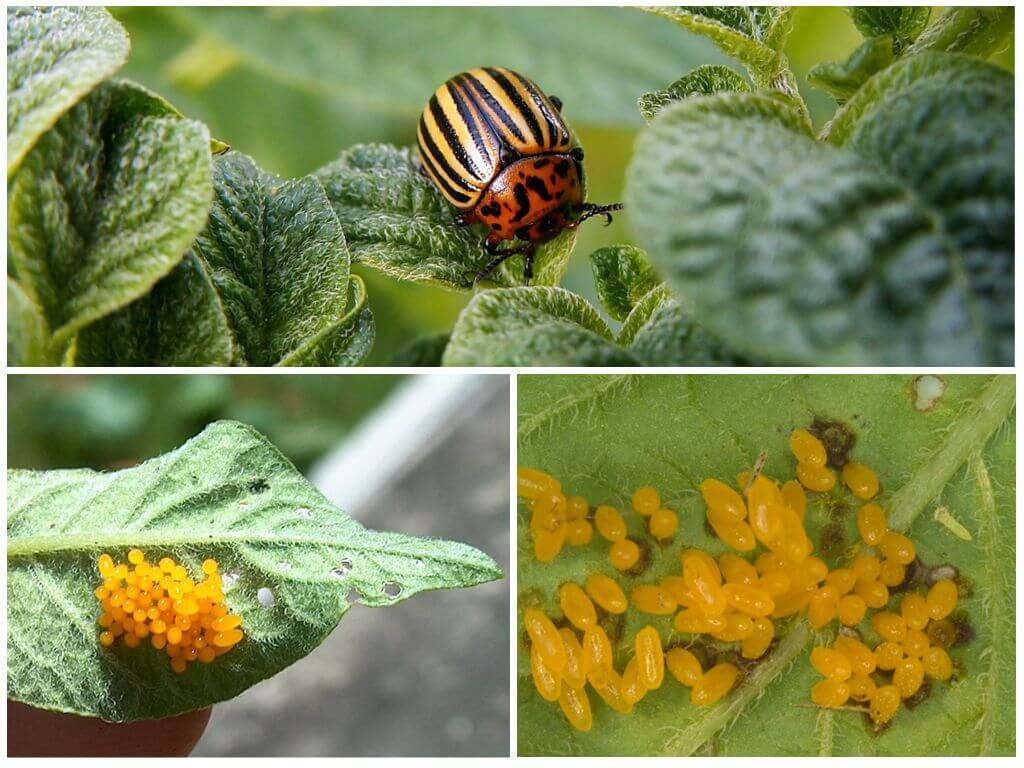
- Insects are orange color modified wings, tight to the calf. On each wing there are five black stripes. By this color of the Colorado beetles is easy to find out.
- In the length of the calf can reach 15 mm, in width - 7 mm.
- If you look closely at the photo of the Colorado potato beetle, you can see that it has a convex part above and a flat one below.
- The insect's rounded, inverted head is very small, much smaller than the body. On her sides are black eyes. The organs of touch are the antennae consisting of 11 segments.
- The abdomen is decorated with black specks arranged in rows.
- The paws, in the amount of three pairs, are poorly developed in the beetle.They have peculiar hooks, thanks to which the pest crawls easily through the leaves.
Interesting!
The Colorado potato beetle flies thanks to webbed, well-developed wings. He easily makes long-haul flights, learning new habitats. Flying beetles make only in warm weather, before they have to winter.
Development with the transformation of the Colorado potato beetle
With the onset of spring, Colorado beetles crawl to the surface. After 5-6 days, their reproduction begins. This process continues until autumn. After mating, the females find secluded places and hide the eggs of the Colorado potato beetle in them. Their number varies from 20 to 70 pieces. Male and female mate most intensively in sunny clear weather. Most often this occurs in the afternoon or midday hours.
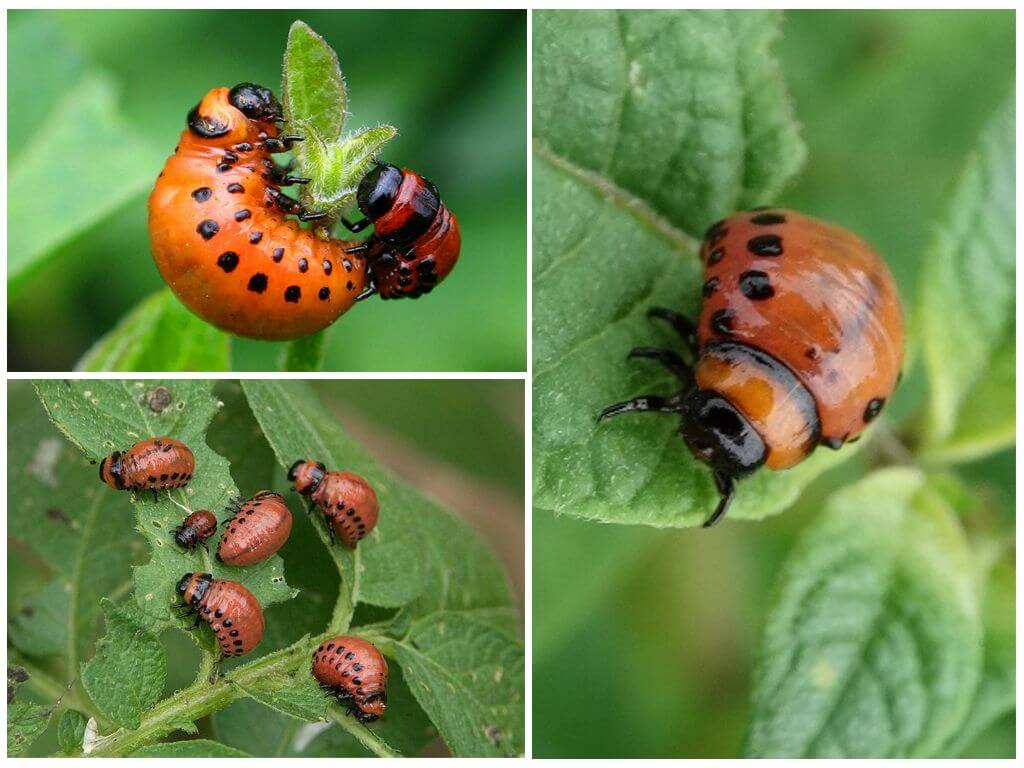
Eggs can be seen on the leaves (on the reverse side), as well as on the shoots. Larvae appear after 7-21 days. They undergo a pupation process and with the onset of summer time they turn into adult individuals. If you look at the photo of the Colorado potato beetle, you can clearly see the curved back of the red-orange color, which changes as it matures.It turns orange with a yellowish tint.
On a note!
The feature of the larvae is the presence on the sides of two rows of black dots. They are very voracious, but initially they feed only on the flesh of the plants, subsequently they completely eat the shoots. Therefore, the fight against the larvae of the Colorado potato beetle in gardens and fields is inevitable, as this will help preserve the crop.
There are various methods of their destruction: mechanical, biological, agrotechnical using chemical preparations. As a result of the actions taken by the human beetles must die.
Life cycle
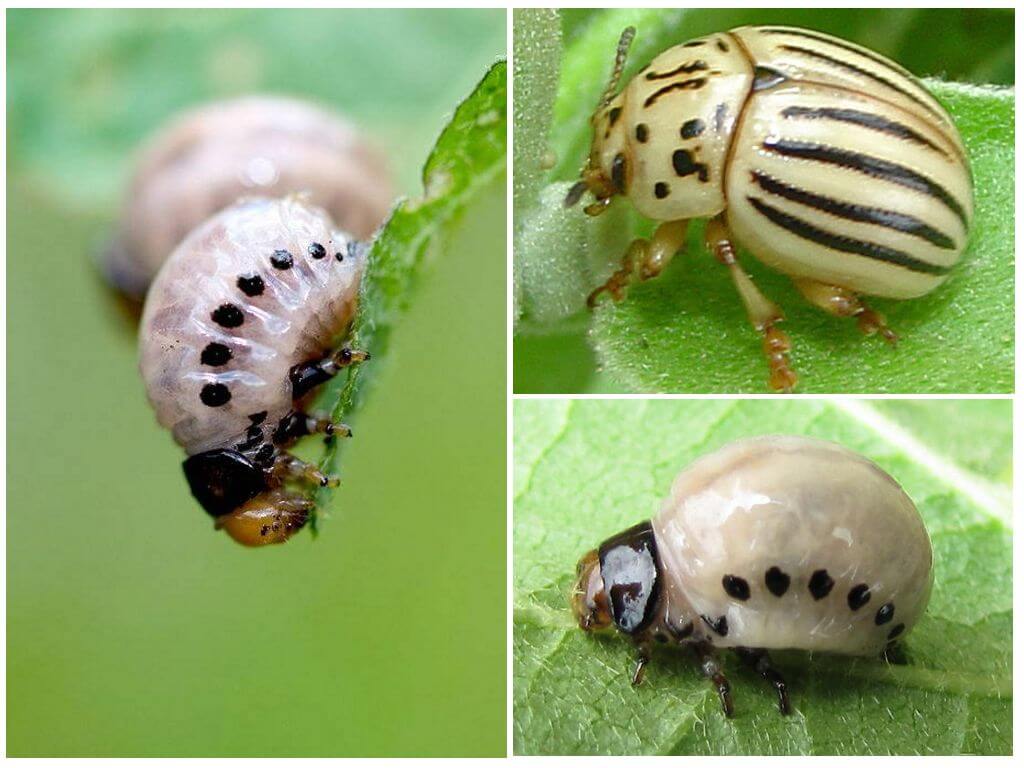
If the fertilization of the female occurred in the autumn period, she lays her eggs in the spring, immediately after wintering. The larvae appear in 14-21 days. Feature of development - insects pass through 4 stages of development of the Colorado potato beetle:
- The body, densely covered with hairs, has a gray color. The body in length reaches 2.5 mm, eats the pulp of young leaves.
- Body hair slightly lowered, body length increases to 4.5 mm. At this stage, the larva feeds on the leaves themselves, but only on its soft part.
- The body acquires an orange color, the length increases to 9 mm.
- At the last stage, the color changes, it acquires reddish-yellowish shades. The body can have a length of from 10 to 15 mm. This cycle of development in the larva is the most voracious.
In the stage of the imago, the Colorado beetle eats very richly. He almost completely destroys all the foliage, making himself nutritional reserves. The larvae hide 10-15 cm under the ground for further pupation. This process can last up to 18 days and it depends on what the temperature of the soil.
Wintering features
During pupation in the autumn period, the Colorado potato beetle hibernates in the ground, appearing to the surface. Adults can withstand temperatures up to -9 ° C. If the ground is sandy, the depth of their maturation reaches up to half a meter. In winter, the Colorado beetles sleep long, some individuals die if the frost is very strong. The female endures wintering worse if she has already laid eggs, as she lacks fat reserves. In spring and summer they appear on the surface of the soil, where their transformation takes place. They begin to wake up when the temperature of the earth warms to 14 ° C and the air reaches 15 ° C.
In hot and dry periods, the Colorado beetles often fall asleep. They can sleep for almost a month, after that their life is reborn again, and they can multiply.
Important!
Effective time for fight against colorado beetles is the first and second stages of its development. This is due to the fact that the pupa and the adult individual are not so strongly affected by chemicals.
Pest eggs
Few are interested in how long the Colorado potato beetle lives. On average, he lives for 1 year. But some individuals can live up to 3 years. Only in one season, the female can lay up to 1000 oval-shaped eggs, up to 2 eggs long, and up to 3 millimeters wide. Their color is light yellow and bright orange. Older females lay darker eggs. Air temperature conducive to the appearance of larvae should not be below 15 ° C. Colorado beetles are sensitive to low temperatures. Therefore, in a harsh winter, depending on the type and soil moisture, individual insects and, accordingly, the eggs of the Colorado potato beetle die at temperatures from -9 to -11 ° C for the first six hours.
Interesting!
Insect sensitivity to cold occurs 3 times a year, many of them die. First, increased mortality is observed in the period September-October. At this time, the vegetation of potatoes has already ended and the Colorado beetles, including females, who have late elated, did not receive the necessary supply of food. They burrow into the soil and with the onset of cold weather, many of them die. The second period falls on the second half of November and the beginning of December. At this time, the state of physiological dormancy (diapause) in pests has ended, the body’s resistance decreases, and the defensive reactions from the cold are still weak. This all together leads to the death of the Colorado beetles. The third period begins with the arrival of spring - in March and April. During this period, insects prepare for awakening. Their death occurs for various reasons: due to the defeat of the body by fungi and bacteria, exhaustion and the sudden onset of cold weather.
False Colorado potato beetle
Such an insect is sometimes found in Russian regions. It is very similar to the present Colorado potato beetle in appearance, but unlike it, it is not dangerous.Its color is more faded, and the stripes on the back are white. Food for him are the weeds of the family of solanaceous plants. Potato tubers do not attract him. Therefore, the insect of this species is often called the false potato beetle. It can not be destroyed, as it does not cause damage to agriculture.
Natural enemies
The Colorado potato beetle, like other insects, has its own natural "enemies", for which they become a tasty prey. These include:
- Domestic bird. Homeowners engaged in the cultivation and breeding of turkeys and guinea fowls, can safely let them into the garden. They gladly eat the larvae that are on the leaf.
- Bugs - podizus and perillus. They and their larvae feed on the eggs of the Colorado beetles.
- Flies of the genus Doreophagus. They lay their larvae in the body of beetles. But in a harsh climate flies do not live.
- Grasshoppers. More than 50 species of them live on the territory of the Russian Federation; almost all of them are illegible in food; they don’t let the Colorado beetle larvae pass through.
It is likely that horticultural friends and some species of insects will greatly assist vegetable growers in pest control.
How bugs appear on the plots and what they eat
The owners of cottages and country houses engaged in the cultivation of crops are wondering how the Colorado potato beetle got to them. Definitely no one can answer this question. We can say that they moved from a neighboring area, they were attracted by the smell of potatoes. And he acts on them as on cats valerian. Therefore, the best thing you can do is to unite with your neighbors in the fight against them.
Interesting!
The Colorado potato beetle, in addition to potatoes, eats other crops grown by vegetable growers. If their favorite delicacy is not enough, they get over to tomatoes and eggplantseating all their leaves. Wild Solanaceae, they also eat and accumulate in their body toxic substances contained in plants. Therefore, birds of prey do not attract the larvae. They are eaten only by turkeys and guinea fowls.
Some owners of suburban real estate bred on their sites a perennial shrub called ashwagandha. In India, it is called the root of life, because it has healing properties. Therefore, the question of whether ashwagandhu eat Colorado beetles is quite relevant.The shrub belongs to the family of solanaceous plants, like tomatoes, eggplants, and pepper, therefore it is of interest to the Colorado beetles.