Description and photo of the fly fly zhigalki
Content
- Fly zhigalka
- Reproduction flies zigalki
- Diseases transmitted zhigalkoy
Many species of flies adapted to life next to a person. Among the relatively harmless room and there is one small, modest gray fly of a small size that can do much more harm. This is a fly zhigalka - an obligate bloodsucker.
On a note!
Zhigalka is also a synanthropic type of flies that lives alongside human habitation. Together with the man spread to all continents. Sometimes a fly is called an autumn fly, since they become especially noticeable in the fall,when their population increases significantly due to new flies that have developed over the summer.
Habitats
Main food source for zhigalok - livestock. Zhigalok larvae develop in animal manure. Therefore, the main habitat of zhigalok is premises for cattle. Since the cattle are usually located in the same compound as a residential house, flighters can fly into homes where they attack people.
On a note!
Due to the predilection for human settlements, it received the additional name “village fly”. In fact, this type does not exist. So called any synanthropic Diptera speciesholding near villages and villages.
Appearance
In the photo, flies are almost indistinguishable from ordinary house flies. This is explained by the fact that both species are very close in morphology and biology. The average body length of this species of flies is 7 mm. Zhigalka has a gray color with dark stripes on the chest and spots on the belly. The yellowish color of the lower part of the abdomen, like that of a room fly, is absent.
Like the room fly, the male from the female at the fly can be distinguished by the distance between the eyes and the size of the insect. The female has wider eyes and is larger.
There is a scuffle and differences:
- in a restful state, the wings of the whisk are wider apart;
- the proboscis is directed forward like the proboscis of a tsetse fly.
The proboscis is adapted for feeding with blood and has chitinous “teeth” at the end for penetration into the blood vessels and sucking plates for feeding. Both the female and the male feed with blood.
Way of feeding
In the usual understanding of this word, we don’t bite. They scrape the proboscis with the upper layer of the epidermis, seeking the appearance of blood. To prevent the blood from coagulating, the flounter starts to scrape poisonous saliva, which causes severe irritation.
On a note!
At one time, the female is able to drink a dose of blood twice her own weight.
Female blood is required to complete the breeding cycle. A hungry fly will not be able to lay eggs. The desire for reproduction is the reason why this species of flies especially bites in the fall.
Zigalki can spend the winter at any stage of development, but already at a temperature below + 8 ° C hibernate. Before wintering, the female should have time to lay eggs. In the southern regions with high air temperature, this species of flies can breed year-round.
Breeding
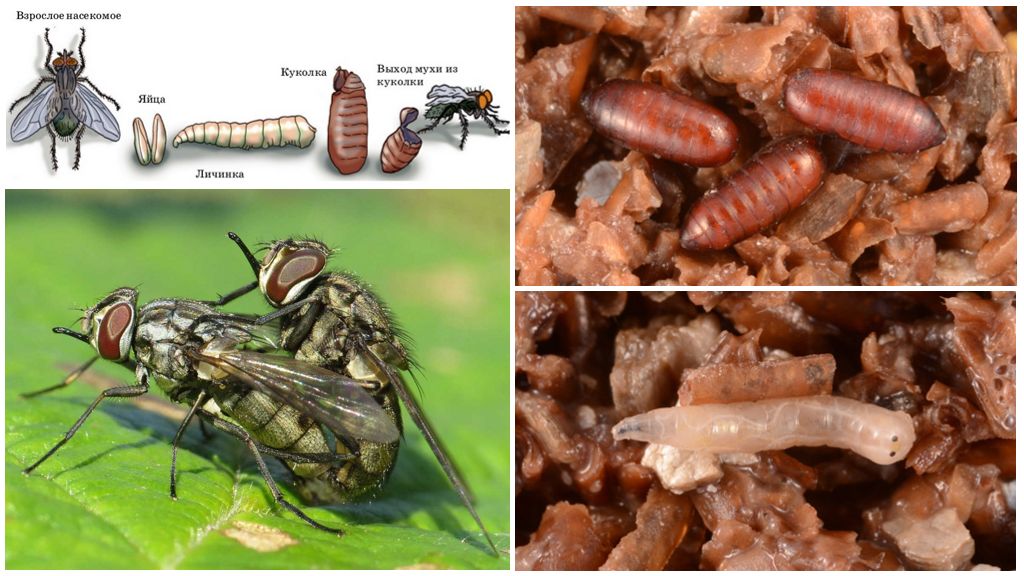
Insects breed very rapidly. To full life cycle they take from 3 to 8 weeks depending on the ambient temperature. On egg development to the larva stage Only 1 day is required.
During her life, the female lays 300-400 eggs in batches of 25 pieces. The reproduction of zhigalok occurs in animal excrement, sometimes in rotting plant debris. But they can also lay eggs in the wounds of animals and humans.
Interesting!
Cases recorded breeding this species outside human settlements. Autumn flighters were found in a pelican colony in the Volga delta.
The larva in its development goes through three stages. At the third stage of development, the moldy worm reaches a length of more than a centimeter and a diameter of 1.2 mm. With age, the shell of the larva grows coarse. At the stage of the third age, the molds of the wormwood take on a brown color. At the end of development, throwing off the last "skin", the larva turns into a pupa. At the optimum temperature of + 27–30 ° C, the larva requires 4-5 days to develop from the time it leaves the egg to pupation.
Before pupation, the maggots are buried in the transforming organic matter to a depth of 50 cm.For the normal development of the pupa, an external temperature of about 25 ° C and humidity from 20 to 40% is required. In case of violation of temperature and humidity regimes, the development of pupae is disturbed.
The pupa is about 6 mm thick with a thickening around the head. The color of the chitinous cover is brown. The insect breathes through spiracles located on the border of the 1st and 2nd segments.
On a note!
In hot weather, the full cycle of development of this insect from the time of egg laying to becoming an imago takes only 6 days.
The development of the pupa lasts from 4 to 7 days. The imago that emerged from the pupa is immediately ready for reproduction.
What is dangerous for humans?
Like any “reusable” bloodsucker, a flint is capable of transmitting dangerous diseases to a person:
- relapsing fever;
- tularemia;
- trypanosomiasis;
- ehrlichiosis;
- anthrax.
Frequently flies sit on decaying carrion, catching pathogenic bacteria on their paws and proboscis. In this case, when fed with blood, they can introduce bacteria into the wound. But the danger of sepsis in this case is minimal. The human body is able to resist a small number of pathogenic bacteria.Microorganisms brought from carrion are dangerous only to people with an inactive immune system.
On a note!
The transfer of dysentery pathogens and helminth eggs is a common function of all flies, including the autumn zhigalka.
What to do when you bite
On the place of the fly bite very often there is severe irritation with swelling of soft tissues. If the fly is bitten by a fly fly, the bite is immediately washed with cold water to reduce skin irritation. If the house has antihistamines, they can be used to relieve an allergic reaction. If there is pain and itching at the site of the bite, you can apply ice, lotion with soda, and other means that can reduce discomfort. Also suitable for anti-insect bites.
The wound must be disinfected. If an allergic reaction at the site of the bite does not pass, it is necessary to consult a doctor.