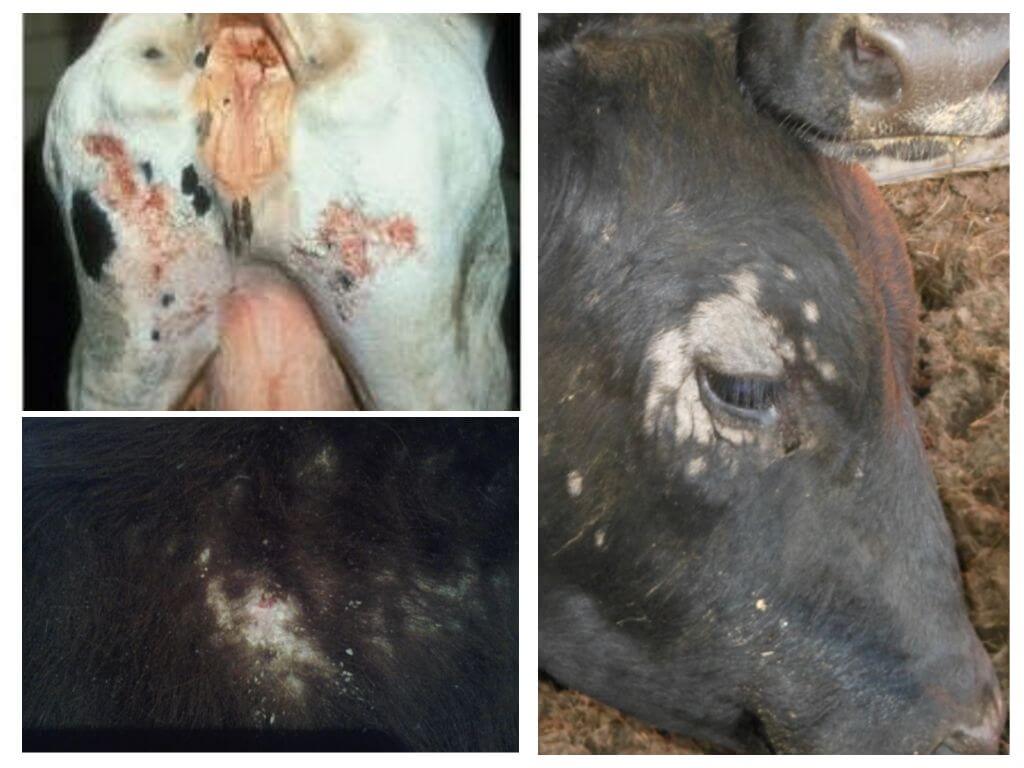
Cows
- Blasters
- Cows
- Remedies for lashing
Vlasoyed cows are also found as often as other warm-blooded animals. They are parasitic insects that feed on particles of the epidermis, cornified cells, lymph and secretions of the sebaceous glands. In nature, there are about two hundred species of insects that parasitology studies. There are dog eaters, cats, rats, sheep and even horses. Cattle are not an exception. Striking the animal's hair, the parasites harm their health, as a result of which the livestock productivity is reduced.Therefore, if you find lashing eaters in cows, you should immediately begin to fight with them.
Features of the lice
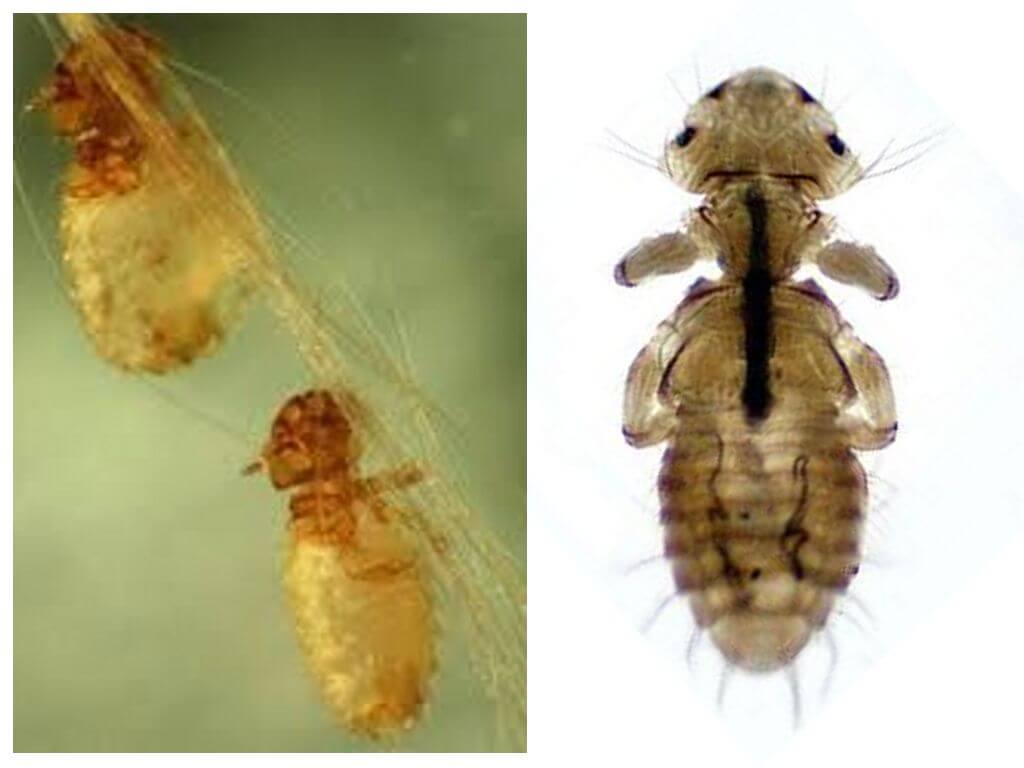
The voyeur is a small wingless insect, whose flattened body is 1-2 mm long. In appearance, it is very reminiscent of the parasitic on cows louse. The only differences are the wide head and the gnawing type of oral organ. The parasite moves with the help of three pairs of legs, at the ends of which there are claws. Thanks to them, the insect is firmly held on the hair of cows. Segmented oval abdomen covered with setae. On head are segmented antennae. The photo of the teeth of the cows is presented below.
Breeding at lashes is bisexual. After mating, the female lays eggs. It attaches them to the hairs of the coat with a special quick-hardening secret of secretions that the glands of the insect produce.
On a note!
One adult female is able to lay about 8-10 dozen eggs.
After about 10 days, the larvae appear on the light, which differ from mature individuals only in size. The adult larva becomes three molts on incident, the period between which makes 10-12 days.
Signs of infection
Particularly active skin parasites show in the autumn-winter period, when the coat of cows is more dense. After all, pests are very afraid of bright light, and dry air is also not desirable for them. In the absence of the owner, the eaters die in 2-3 days. With the arrival of spring, the parasites become smaller as the animals begin to actively shed. In the summer, the body’s resistance increases, as a result of which the skin becomes more elastic and dense, which also affects the number of lashes.
Cows are infected with parasites from their fellows who already have the disease. The reason for the appearance of eaters on the farm is also poor maintenance and non-compliance with sanitary standards.
Symptoms of eaters in cows are as follows:
- severe itching causes skin inflammation and hair loss;
- wool loses a healthy shine and becomes rough to the touch;
- the cow loses its appetite, becomes nervous and irritable, decreases milk yield;
- a decrease in the immune system leads to an exacerbation of chronic diseases, the occurrence of colds and infectious diseases.
On a note!
Blasters are also dangerous because they are carriers of many infections, the consequences of which are helminth, viral, fungal and bacterial diseases.
Treatment methods
Treatment of licefishes in cows is carried out with the use of insecticidal preparations. Therefore, it is very important how and how to treat the animal. After all, the final result of the fight against parasites will depend on the right choice of a chemical agent. It is also worth noting that adult individuals and larvae are more sensitive to insecticides than eggs of parasites.
To cure a cow or calf from lashing, you must:
- Use Neostomazan, Sevin, Oksamat, K-otrin or Dibrom. The solution prepared in accordance with the instructions is treated with animal hair. Similar properties have a solution of Butox or Avertin.
- Also for this purpose mono apply sprays Insektol, Acrodex, Perol or Dermatozol. The average consumption of an aerosol product is 50 ml. If the treatment is carried out in spring or summer, then it should be repeated after 8-12 days, and after 12-16 days in the winter season.
- A good result in the fight against lashing gives 0.5% solution of chlorophos.It is better to treat their cattle in the hot season. After 7 days, the procedure must be repeated. In winter, 3% dust of chlorophos is used, which is simply applied to the wool of a sick cow. The treatment with powdered product should be carried out outside the barn so that the particles of the toxic substance do not get into the feed.
Wood ash is another method of fighting against lashes, which is distinguished by its accessibility and effectiveness. It is enough just to rub it into the skin of the cow.