Ascaris looks, features of the structure
Content
- Roundworm structure
- The life cycle of the parasite
- Signs of worms
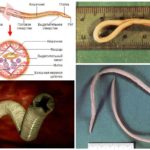
Who are worms roundworm - a large group of roundworms, nematodes, parasitic in humans and some animals. When infected, they develop ascariasis, a dangerous disease with serious consequences. Predominantly representatives of each genus Ascaris amaze a certain species of animals. Worms live in the intestines of the host, often causing death.Human ascaris belongs to the genus Ascaris lumbricoides, it has a distinctive appearance and body structure, which is clearly shown by the photo of ascaris.
Features of appearance and size
Like all roundworms, ascaris has an elongated, smooth body with a spindle-shaped (nite-shaped) shape with pointed ends. In the photo of roundworm it is clearly seen that the color of a living individual varies from red-brown to yellow-pink. The body of the dead parasite acquires a white-yellow color. The round cut of roundworm has a regular round shape. The parasite belongs to dioecious organisms - mature individuals of both sexes participate in the process of reproduction.
On a note!
The size and shape of the roundworm is related to gender. In males, one end of the body is hooked to the abdomen. The body of adult worms is stretched up to 25 cm, in thickness - up to 3 mm. Females exceed them in size, reaching 40 cm in length and 6 mm in cross section.
Anatomical features
Ascarids in the body of an infected person remain viable for 1-3 years. In the absence of external negative factors die from old age.Features of the structure of the roundworm and the structure of the body allow the worms to parasitize in the small intestine for a long time, to penetrate into the bloodstream and internal organs.
Outer shell and skeleton
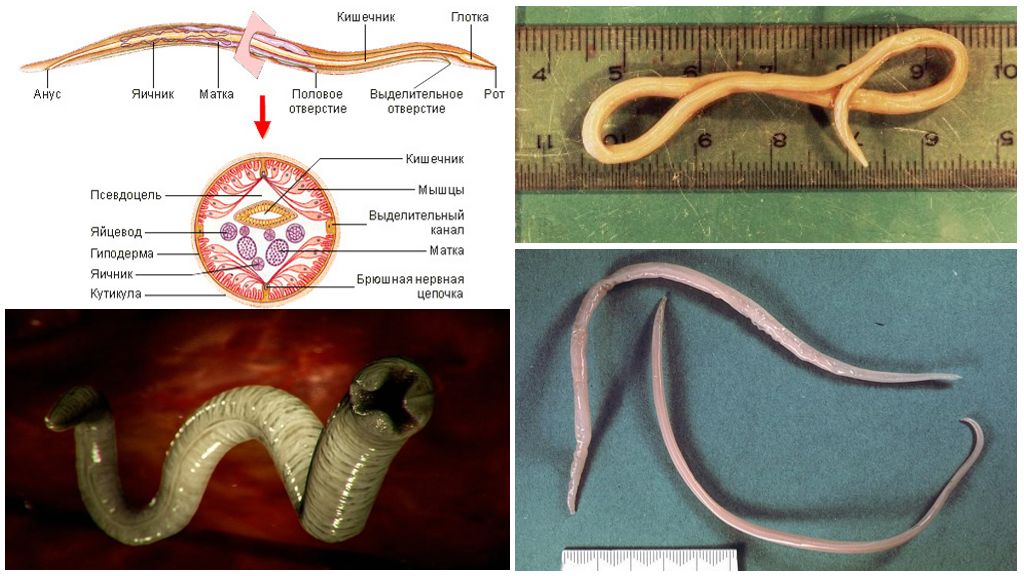
The body of an adult individual is covered with a dense three-layer sheath. In section, it consists of the outer cuticle, the middle epithelial layer, which is firmly connected with the internal longitudinal muscles. Ascaris quickly bends the body and actively moves in the intestinal lumen. The worm is not able to stretch or shorten in length. Thanks to a strong skin-muscular bag, ascaris is reliably protected from mechanical damage and dissolution by digestive enzymes.
On a note!
Under the outer three-layer shell, the cavity of the roundworm body is hidden - free space with internal organs. It is filled with a pressurized aqueous liquid. This is a natural hydro skeleton, which determines the dense structure and constant shape of the body of the roundworm. Nutrients and waste products accumulate in the liquid.
Life systems
Ascaris has no special attachment bodies - hooks or suckers.It is retained by constantly moving in the opposite direction to the food and feces masses. At one end of the parasite's trunk there is an oral opening. It is framed by three constricting lips - cuticular swellings. With their help, the worm is able to pinch the intestinal mucosa and attach to it. In the photo of the helminth you can clearly see what the ascaris looks like. The internal structure of the body of the worm and the characteristics of life systems:
| System | Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Digestive | Behind the mouth opening begins the throat - a powerful cylindrical muscular organ. Next comes the midgut (esophagus) of flattened form with transverse striation. It smoothly passes into the main intestine (through hollow tube without branches), stretched along the whole body. In males, the posterior intestine ends in a cloaca, in females the anal opening (anus) in the abdominal part. |
| Excretory system | It consists of four phagocytic cells and two tubules. Brown cells are located on the inside of the front part of the body. The canaliculi stretch to the right and left sides of the body, blindly ending at one end.The other ends are connected and opened by a hole on the ventral side. The organs of excretion are in direct contact with the cavity fluid, absorb waste products from it and remove them. |
| Nervous | Type of nervous system ascaris relatively developed. It includes a pharyngeal ring with a thick nerve trunk extending to the abdominal side. There are poorly developed longitudinal branches to the internal organs and the trunk in the dorsal region. Ascaris has tactile feelings. In males, they are provided with preanal and postanal papillae in the caudal part of the body. |
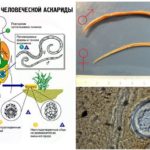
| Sexual (in females) | It is represented by the thinnest paired ovaries of the thread-like form, oviducts and uterus. Both tubular systems are connected to an unpaired vagina, which opens to the outside with one hole (vulva) in the anterior third of the female's body. The total length of the system tubes is many times the size of the roundworm body. Up to 25 million eggs can develop simultaneously in its reproductive system. |
| Sexual (males) | Unpaired, is represented by filamentous thin testes, dilated vas deferens and ejaculating channel. The latter falls into the cesspool.Attaching to the body of the female and ejaculation occurs due to the spicules - paired cuticular growths with a length of at least 2 mm. |
| Respiratory | When asked what the helminth breathes, the answer is negative - breathing is not carried out in a roundworm. The parasitic lifestyle in an anaerobic environment (without oxygen) determines the absence of the respiratory organs of the worm. Metabolism and energy release occurs due to cavity fluid. |
On a note!
In the photo roundworm with symbols all the vital systems and organs, signs of sexual demorphism are clearly indicated. After fertilization, the males die and are removed from the feces. Females continue to live, breed.
Habitat and reproduction
Roundworm parasites are found in primates, pigs, some birds, cats, dogs. These types of worms do not pose a threat to humans. The disease develops in children and adults solely by ingesting the eggs of human roundworm. Man is the only and final host in whose body the helminth undergoes metamorphosis from the larva to the adult.
On a note!
Ascariasis develops only when ingested invasive (infectious) eggs of the parasite with a mature larva. In other cases, the infection does not occur.
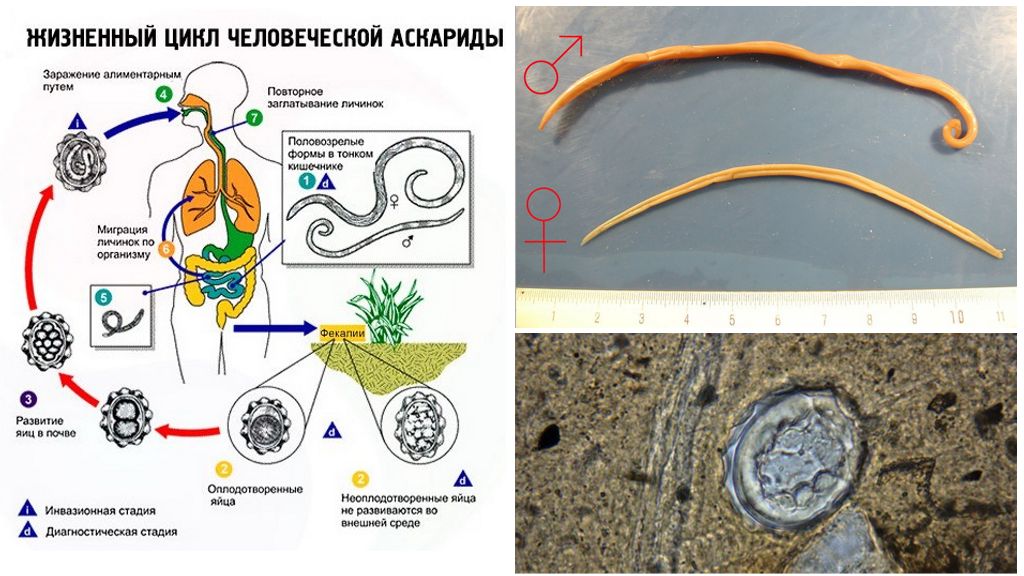
Life cycle
What are roundworms are parasitic nematodes with a closed life cycle. The general scheme of helminth development includes the following stages:
- hatching of larvae from eggs, colonization of an infected person by them;
- early migration stage - small larvae drill the intestinal wall and penetrate into the blood;
- with the bloodstream, they are spread to different organs (heart, lungs, liver);
- mature larvae migrate from the bronchioles to the trachea, are swallowed again in the oral cavity;
- late stage - the larvae re-enter the small intestine and reach maturity here;
- fertilization of the female laying up to 250 thousand eggs daily;
- Ascaris eggs in the feces pollute the environment.
The total duration of metamorphosis is up to 3 months. During the entire migration period, the length of the roundworm increases to 10 times.
On a note!
To achieve an invasive stage, parasite eggs require suitable conditions — soil, humidity up to 8–10%, and temperature in the range of 16–26 degrees. When these parameters are saved, the larvae form within 2-3 weeks. In favorable habitats, they remain viable for a long time.
Main infection routes
The roundworm lacks the circulatory system and gas exchange processes. In the presence of oxygen, the adult dies; therefore, the main sources of infection are the eggs and larvae of the helminth. They enter the human body with soil particles, poorly washed vegetables and dirty fruit. The risk of infection increases in violation of the rules of personal hygiene and sanitation. Small children, workers in agriculture and sewage treatment plants, summer residents, and residents of agrarian areas are most susceptible to ascariasis.
Symptoms and treatment
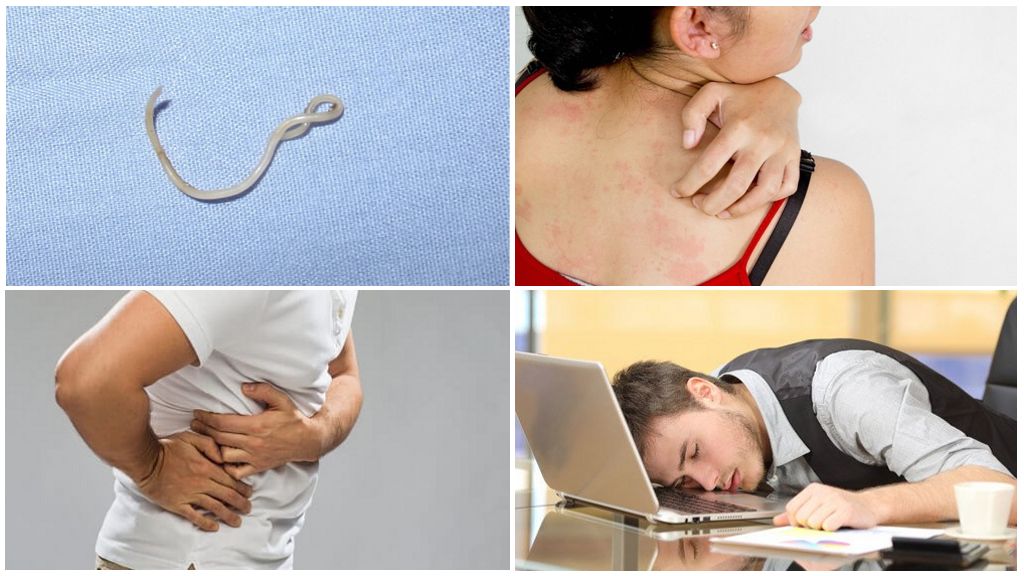
The simplified digestive system of roundworm allows it to feed on semi-digested food masses and the mucous membrane of the human intestine. In the process of development of the larva, intoxication of the infected organism occurs. Ascariasis at this stage is characterized by common signs of sensitization and damage to internal organs.
Description of symptoms:
- allergic rashes;
- itching, shortness of breath, pleurisy;
- general malaise, weakness;
- pain in the hypochondrium;
- colic in the liver, kidneys.
At a late stage, adult roundworms actively grow, multiply, colonize the intestinal cavity.Intensive vital activity of the helminth is accompanied by a number of symptoms:
- nausea, vomiting, constipation, flatulence;
- intestinal obstruction, diarrhea;
- loss of appetite, weight loss.
Complications of ascariasis are expressed in serious damage to the internal organs, and they are fatal. Treatment of the disease - a long, systematic, using antihelminthic drugs. If it is necessary to remove the larvae, surgical methods are used to extract the parasite from the affected organs. Competent therapy allows you to get rid of the parasite and the consequences of ascariasis. In order to avoid relapse, preventive measures should be taken.