The scheme of the life cycle of the development of human roundworm
Content
- Life cycle of human roundworm
- Roundworm and their eggs
- Roundworm and their eggs
Human roundworms have a parasitic lifestyle, causing a serious disease of ascariasis. All metamorphosis takes place in the body of the main and only host - a person. The life cycle of a human roundworm consists of several stages,transformations from an egg to a mature individual. Each stage is characterized by specific symptoms and requires timely treatment.
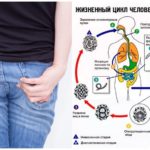
General scheme of development
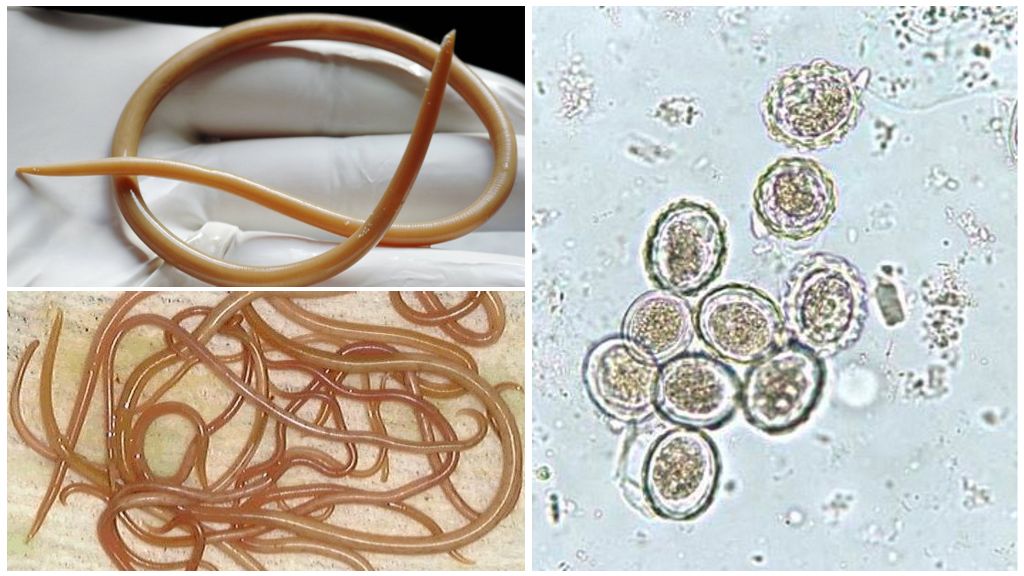
Adult ascarids live in the lumen of the human small intestine. For 1-2 years of their life, they totally affect the digestive tract and internal organs. In the reproductive system of female roundworm contains up to 25 million eggs. Every day, up to 250 thousand fertilized eggs enter the human intestines. They are mixed with feces and released into the environment. From this moment begins the life cycle of the helminth. The general scheme of the development of roundworm:
- The maturation of eggs in the soil (invasive stage).
- Penetration of a mature egg with a larva into the intestines of a person.
- Hatching of the larvae with access to the bloodstream.
- Migration of larvae into internal organs.
- Secondary ingestion of the larvae and the beginning of the intestinal stage.
- Formation of a mature individual.
Main stages and relocation
Human ascaris goes through several stages of development, overcoming a long path in the host organism. During this time, the parasite acquires characteristic anatomical features,determining its long-term viability in the human body.
| Stage | Habitat moving |
|---|---|
| Egg | The external environment is soil. When ingested, enters the intestine. |
| Early larva | It hatches, rushes with the blood flow to the liver, heart, lungs. |
| Mature larva | It forms in the lungs, grows, moves from the alveoli to the pharynx, then back to the intestinal tract. |
| Adult | Lives in the small intestine. |
Egg stage in soil
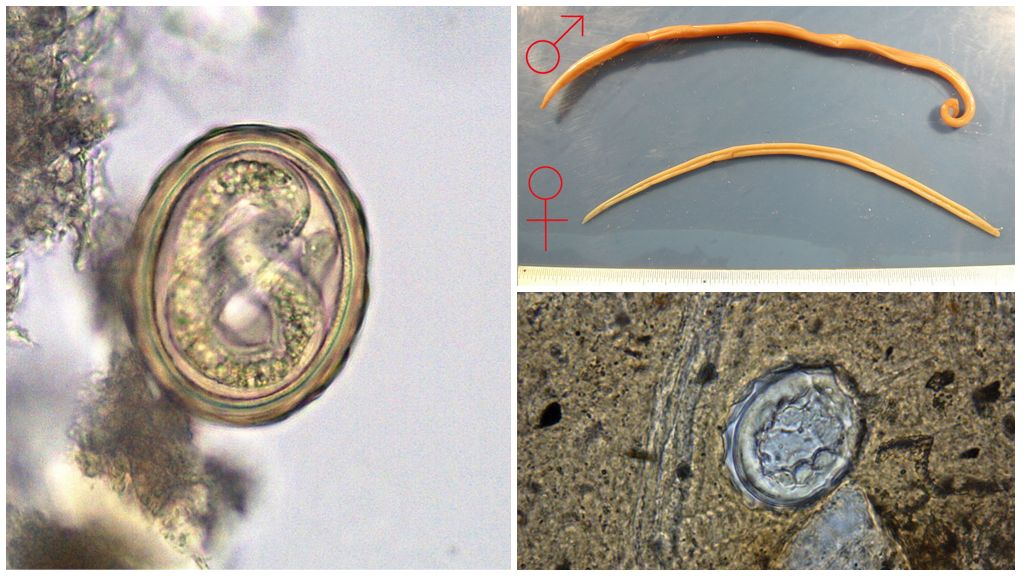
Maturation of roundworm eggs occurs in the environment - soil or water. For further development, they need oxygen, optimal humidity up to 10% and temperature in the range of 16-25 ° C. Under favorable conditions, larvae form inside the eggs within 15–20 days from the blastomeres. Embryos originate in fertilized eggs, where the larva develops. The unfertilized do not develop, die.
Eggs become invasive (infectious) when the larvae acquire sufficient mobility.
Important!
Dense outer shell reliably protects them from external factors. The infectious ability of the larvae in the state of anabiosis lasts up to 7-12 years. When invasive eggs enter the human intestinal tract, the main stages of helminth development begin.
Early migration stage
Larvae occupy an important place in the scheme of development of ascaris.The structure of their body and functionality are different from the adult. For full maturation and metamorphosis they need oxygen. To this end, they long migrate through the human body and penetrate into the lungs, where there is enough air. The sequence of development of ascaris, starting from the egg to the formation of a young larva:
- Swallowed invasive eggs with food enter the stomach, then the intestines.
- Under the action of enzymes, the shell of eggs dissolves, freeing the larvae (about 0.2 mm).
- They are attached to the intestinal wall with tenacious hook-shaped processes.
- Mouth opening and solvent enzymes they puncture the hole.
- Go out into the bloodstream and feed on blood cells.
- The bloodstream migrates through the vessels of the liver, heart.
- Reach the pulmonary artery, alveoli and bronchioles.
- After 10 days, increase in size to 1.4 mm.
- Pushed into the trachea and pharynx, re-ingested into the stomach.
Important!
Ascarid larvae rush to the organs most saturated with oxygen. Individuals that enter the liver and other organs, lose the ability to protravlivaniyu tissues and vessel walls.Here they are destroyed by phagocytic cells or encapsulated, eliminated by leukocytes. Only those that have penetrated the pulmonary alveoli remain viable.
Molting procedure
In the early migration period, the larvae parasitize, since they actively feed on blood cells. During this time, they undergo 4 molts - the process of losing and changing the shell. The first molt occurs in the blood stream in the liver, the second - in the pulmonary alveoli. The third and fourth occur in the intestinal tract after repeated ingestion. Upon completion of the last molt in the life cycle of the development of ascaris, the larva is completely transformed into an adult.
Intestinal stage
Moving through the stomach into the intestine after re-ingestion is the last step in the migration of larvae in the human body. The increased size does not allow them to drill holes and re-enter the bloodstream. The small intestine becomes a permanent habitat and the formation of an adult roundworm.
On a note!
The total duration of metamorphosis with the correct sequence of stages of migration is up to 2-3 months.
Achievement of puberty
The larvae, past the entire sequence of stages of development, acquire the features of an adult roundworm. They vigorously feed on intestinal food masses, they grow rapidly. In a short period of time, young individuals significantly increase in size.
Important!
The body length of males with a characteristic striated pattern is up to 25 cm, the size of females is up to 40 cm. In 4-6 weeks they reach maturity and are ready for reproduction.
After fertilization, males die, and up to 25 million eggs form in the genitals of the female roundworm. Daily clutch is up to 250 thousand. Adult females breed in the human body during the entire period of their life (about 1-2 years). In the absence of treatment, the ascarids live a long time, as nature allows them, they die of old age. With faeces, the eggs enter the environment, ripen to the invasive stage.
Ways of infection, symptoms and treatment of ascariasis
Predominantly infection with human ascaris occurs by the alimentary (oral-fecal) method. Invasive eggs are swallowed with soil particles when using unwashed vegetables and fruits, water from reservoirs, through dirty hands.Most often ascariasis is exposed to children, gardeners, employees of sewage treatment plants. The stages of the sequence of the movement of ascaris through the body of a person are accompanied by characteristic symptoms:
- at the migration stage - pain in the liver, heart, allergies, cough, spasms, intestinal bleeding;
- intestinal stage - constipation, indigestion, diarrhea, bloating;
- reproduction of mature individuals - loss of appetite, weight loss, immunity.
Symptomatology depends on the form, degree of neglect, the number of worms. Multiple damage to internal organs, accumulations of adults in the intestines cause large-scale intoxication of the body and can cause a fatal outcome. Ascarids parasitize for a long time after the start of treatment. Only the combined therapy of ascariasis allows you to finally get rid of all forms of helminth, to avoid relapses and re-self-infection.
On a note!
Domestic pets also suffer from ascariasis, but they are affected by their types of helminths. However, do not underestimate the danger of ascaris in cats for humans. Helminths also penetrate the intestinal tract and other human organs, which is accompanied by intoxication,cough But the completion of the life cycle in the intermediate host organism is excluded.