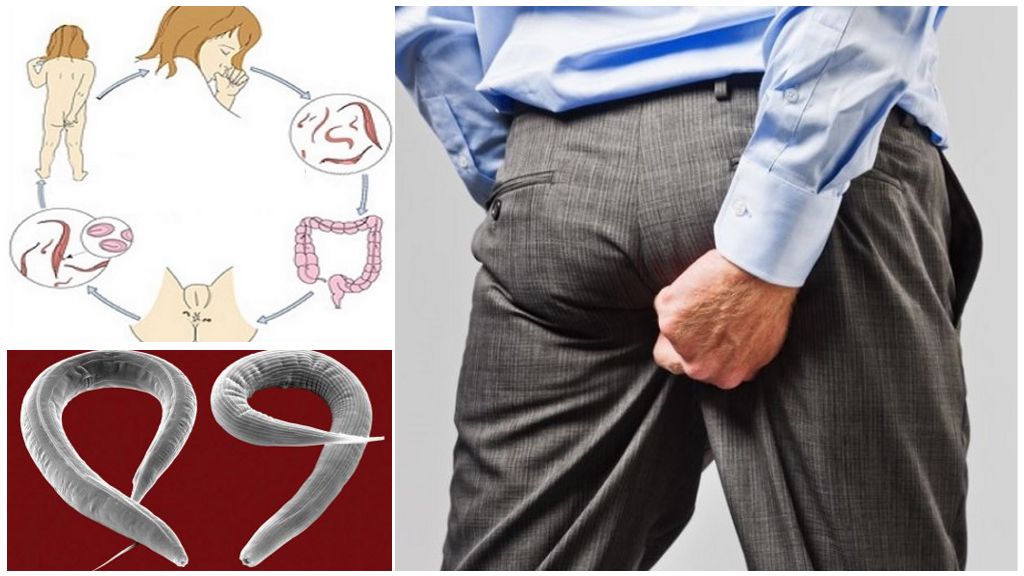
The development cycle of pinworms
Content
- 1 The appearance and anatomy of the pinworm
- 2 Pinworm life cycle begins with infection
- 3 Stages of development of pinworms
- 4 Stage 1 - Formation of Larvae
- 5 Stage 2 - adults
- 6 Stage 3 - Fertilization
- 7 Stage 4 - laying eggs
- 8 Stage 5 - Formation of Larvae and Reinfection
- 9 Consequences of helminthic invasion
- 10 Preventive measures
Enterobiasis is a human infection with pinworms - helminths from the class of roundworms. The disease most often affects children, occurs in adults. The life cycle of the pinworm is short, begins and ends in the human body.Compliance with sanitary norms and rules of personal hygiene prevents re-infection, eliminates the likelihood of the development of dangerous complications of enterobiasis.
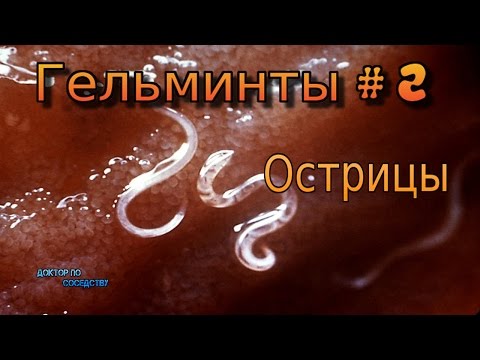
The appearance and anatomy of the pinworm
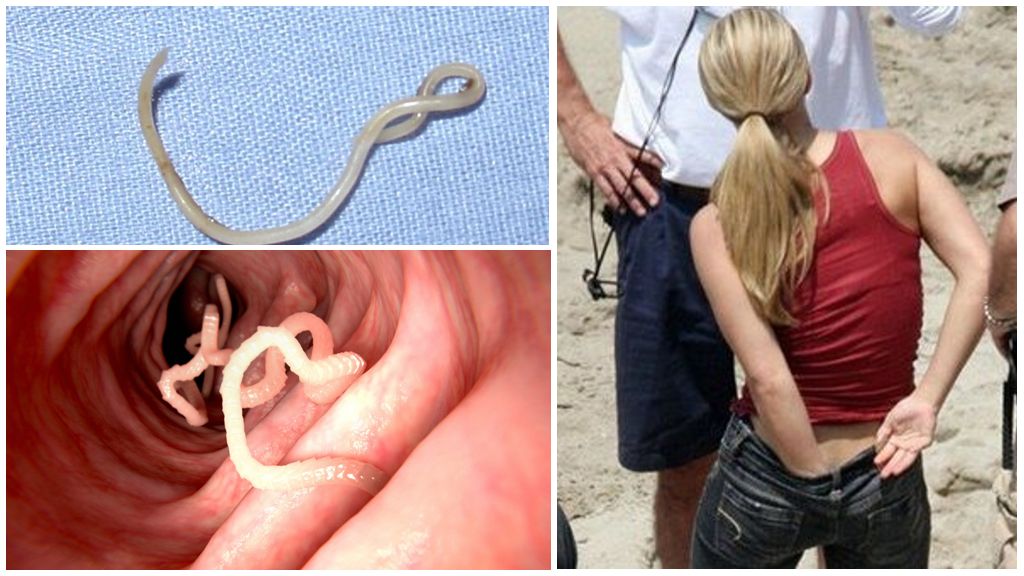
The parasite has a characteristic thread-like shape, white color and a circular cross-section. One end of the torso of females is pointed, which gave the name to the helminth. The other end has a thickening - oral part (vesicle). With its help, the female worm is firmly attached to the intestinal wall of an infected person. The body of males is rounded on both sides and usually twisted in the form of a snail. The size of the body of pinworms has a gender difference:
- the length of the torso of males is 3-5 mm;
- females are thicker and longer - up to 10-13 mm in length.
The colorless, transparent helminth eggs of irregular oval shape are flattened on one side. They have microscopic dimensions up to 0.02-0.04 mm. They can not be seen with the naked eye - only in the field of view of the microscope. The parasite lives and actively reproduces in the human intestinal tract, feeding on nutrients and microflora. In colloquial helminths of this type are called worms or pinworms.
On a note!
In the absence of treatment there is a strong invasion with a long stay of the helminth in the human body. For a long time there is a repeated change of generations of pinworms and serious damage to vital organs. A person is able to infect all the surrounding family members, collective.
Pinworm life cycle begins with infection
Enterobiasis suffers only from a person whose body is the sole host for helminths. The disease begins with the ingestion of parasite eggs. Adults of a worm cannot live outside the host’s organism and immediately die in the environment. Their entry into the human digestive tract is a prerequisite for the life cycle of pinworms. The main ways of infection with worms eggs:
- through direct contact with an infected person;
- breathing in air mixed with dust and eggs of the parasite;
- touch with various objects - bedding, furniture, plumbing;
- consumption of water, food products with pinworm eggs;
- the carrier may be pet hair;
- children are infected through common toys, clothes, dishes.
On a note!
Pinworm eggs outside of a person live for 2-3 weeks on items. They are covered with a dense shell that protects against environmental influences. It allows them to maintain their viability for a long time under the condition of high humidity and optimum temperature (10-15 ° C) of air. Pinworm eggs die when the temperature rises to 50-60⁰С.
Stages of development of pinworms
Predominantly infection occurs with multiple helminth eggs. When ingested, they come from the mouth with food or saliva into the stomach, then into the intestine. Here in the human body pinworm goes through all stages of development:
- release of larvae from the egg;
- grub ripening;
- the formation of adult individuals;
- fertilization;
- egg laying;
- appearance of larvae;
- reinfection
Important!
The complete development cycle of pinworms after ingesting eggs is 3-4 weeks. The same lasts for the incubation period during which the person does not notice signs of helminthic invasion. Most often, the results of the life of the helminth are found at the stage of laying eggs.
Stage 1 - Formation of Larvae
The life cycle of a child's pinworm begins with the entry of helminth eggs into the small intestine. Here, under the action of digestive enzymes, their dense protective shell is destroyed. Moving larvae are released into the intestinal cavity, which feed on and actively grow. During this period, the infected person feels the first signs of indisposition - weakness, fatigue, intoxication. Growing larvae secrete enzymes that have a toxic effect on the human body.
Stage 2 - adults
Within 2 weeks, the larvae gradually move from the duodenum to the upper part of the large intestine. At this stage of development of pinworms, adult individuals are formed, reaching sexual maturity and the ability to reproduce offspring. They attach to the intestinal wall, causing point hemorrhages, inflammations, symptoms of dysbiosis or food poisoning.
Stage 3 - Fertilization
After the transformation of the larva into an adult, an important stage begins in the life cycle of the pinworm - fertilization of the females. Immediately after this process is over, the males die. Females remain in the colon, waiting for the uterus to fill with eggs.
Stage 4 - laying eggs
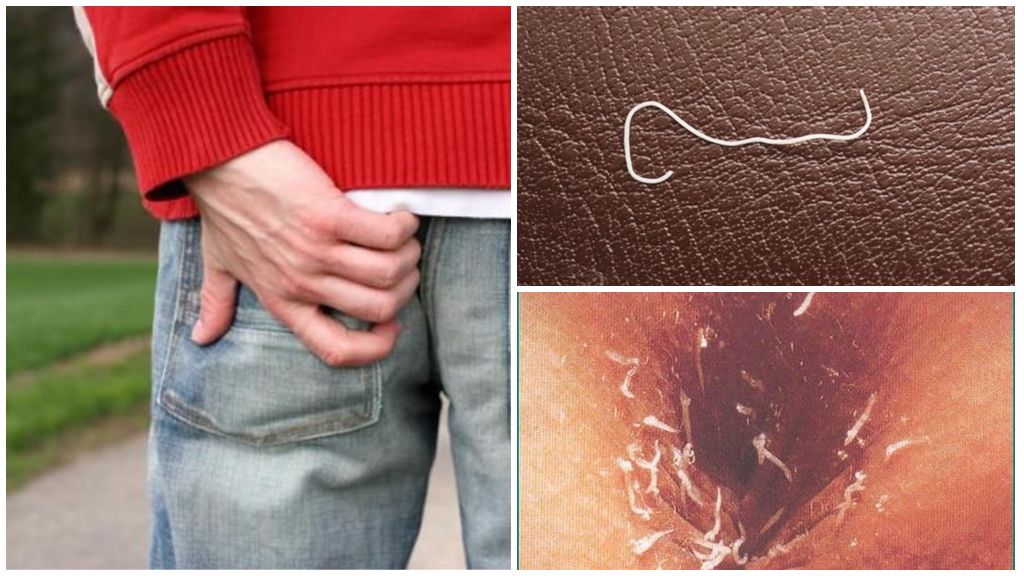
For effective treatment of enterobiosis, it is necessary to know how many pinworms live in the human body. Females filled with eggs break away from the intestinal wall and gradually move into the rectum. In search of a place for laying they go outside. The most common sites for the deposition of worms eggs:
- anal folds;
- gluteal folds, crotch;
- vagina and genital area.
Important!
The number of eggs laid by one female is on average from 13 to 20 thousand. Most often this process occurs at night when the sphincter muscles are relaxed. After laying the female pinworms die, turning into an amorphous mass. Eggs are excreted with a special mucus that causes severe itching and burning in the anal area. When combing, they fall under the nails, bedding, personal hygiene items.
Stage 5 - Formation of Larvae and Reinfection
At high humidity and a temperature of 35-36⁰C, the duration of maturation of laid eggs is up to 4-6 hours. If the rules of personal hygiene are not followed, the larvae appear from them, which penetrate back into the rectum and large intestine.When eggs are introduced into the oral cavity, reinvasion occurs - the cycle of the life-cycle of pinworms repeats.
The duration of the entire development of the helminth from swallowing eggs to the death of adults is up to 1 month. A strong worm infestation is delayed for several months, causing a serious intoxication of the body. The risk of helminth infection persists for 2-3 weeks - this is the answer to the question of how much pinworm eggs live in the environment.
On a note!
Most of the living and killed adults, eggs leave the body of an infected person with feces. Their detection in fecal masses is the main method for the diagnosis of enterobiosis.
Consequences of helminthic invasion
With proper treatment in human body, pinworms live for a short time - a period of not more than 1 month. Long-term recurrent helminthiasis causes dangerous effects:
- the penetration of worms in the pelvic organs, the development of vaginitis, endometritis;
- provokes inflammation of the appendix and the development of appendicitis;
- hit on the bile ducts in the gallbladder, cholecystitis;
- children - absent-mindedness, nervousness, apathy, school failure;
- increased allergies, soreness, weak immunity;
- when penetrating the abdominal cavity - the risk of peritonitis.
Preventive measures
For the prevention of enterobiosis and helminthic re-invasion, an important role is played by preventive measures. To this end, in the scheme for the development of pinworms, it is necessary to prevent the possibility of reinfection with eggs and larvae:
- close personal hygiene;
- regular room sanitation;
- washing vegetables, fruits, herbs before consumption;
- frequent change of bed linen, garments;
- processing of pet hair, furniture, carpets;
- use of disinfectants for cleaning.
Regular preventive examinations with the delivery of feces to the eggs of worms allow you to start treatment in a timely manner and avoid re-invasion. Often, de-worming of all family members, a children's team, is assigned, which allows to get rid of the parasite at any stage of pinworm development.