Where are the Giardia in the human body
Content
- Giardiasis
- Symptoms of intestinal lamblia localization
- Symptoms of lamblia localization in the respiratory system
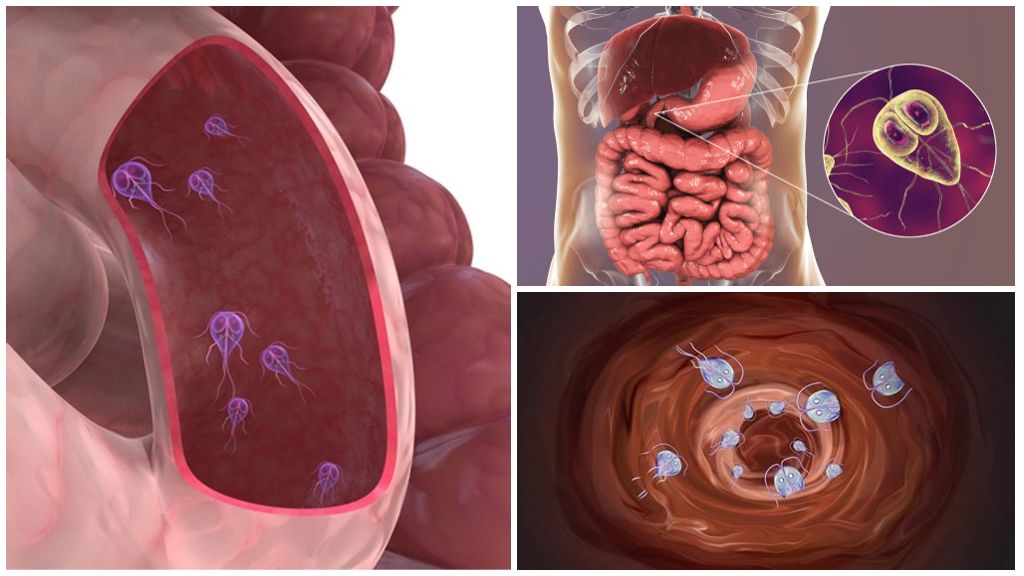
Giardiasis is a dangerous parasitic disease that develops when Giardia is infected. These single-celled creatures of microscopic size settle in the internal organs of a person, causing their disorder and dysfunction. For timely diagnosis and treatment it is necessary to know where Giardia live in the human body.
Features of development and habitat
Giardia - the simplest microorganisms with an anaerobic form of life. In the environment, they are present in the form of fixed cysts (spores), covered with a durable impermeable shell. At this inactive stage, the parasite retains viability and invasive properties for 3-6 months. Translucent cysts have an oval shape, sizes up to 12 microns. Under the shell lies two nuclei and folded flagella.
When cysts enter the human oral cavity, they are swallowed with food and water. Passing through the esophagus and stomach, the parasite spores are transported into the duodenum. Here, in favorable anaerobic conditions, the sheaths of cysts dissolve. Trophozoites, a vegetative form of Giardia, emerge into the intestinal cavity. They are actively moving through two pairs of flagella, attached to the walls of the intestine with a powerful sucker. With no treatment, Giardia has been in the human body for many years.
On a note!
For the development of giardiasis, it is necessary to form at least ten trophozoites in the intestinal cavity. If a person has strong immunity, then cysts and trophozoites without consequences bypass the gastrointestinal tract, are removed from the body with feces.
The main types of giardiasis
Localization of Giardia in the human body determines the symptoms and nature of the course of the disease. Depending on the habitat of the parasite, there are several forms of the disease:
| Giardiasis | Habitat in humans |
|---|---|
| Intestinal type | The lumen of the small, duodenum. |
| Hepatobiliary type | The ducts of the liver, gallbladder, kidneys. |
| Extraintestinal type | Respiratory, urinary, cardiovascular system. |
| Mixed type | In different organs. |
| Chronic | Complex symptoms, similar to the disease of internal systems. |
| Asymptomatic | Symptoms are absent or mild. |
| Acute | Sudden, pronounced signs of the disease. |
On a note!
If Giardia live in children in the body, then Giardiasis takes on an acute course. In a favorable intestinal environment, parasites actively proliferate by simple division. Every 15 minutes, two giardia form from one cell.
Intestinal form
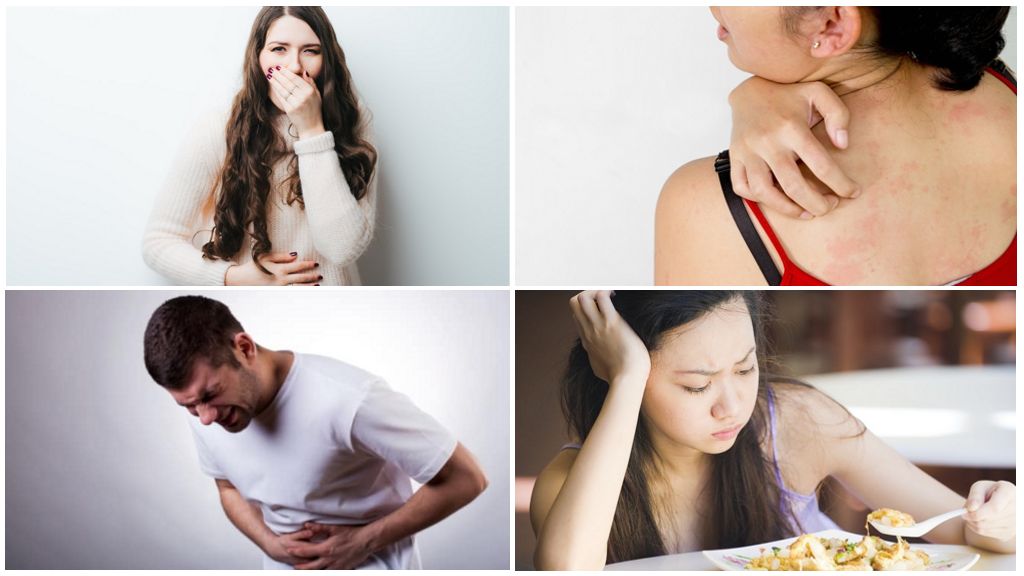
Like all the simplest parasites, Giardia chooses abdominal organs. The lumen of the small intestine is the optimal place for the long-term existence and reproduction of the parasite.Here in a warm, moist environment, trophozoites feed on solutes. They attach to the villi of the intestinal mucosa, provoke inflammatory processes in the epithelial tissue. Symptoms of intestinal lamblia localization:
- nausea, dyspepsia flatulence, vomiting;
- erratic stools, abdominal pain;
- lack of appetite, anemia, weight loss;
- peeling of the skin, pigmentation, rashes.
Giardiasis of this type is often accompanied by enteritis, duodenitis, and enterocolitis. The life span of an adult Giardia in the intestine is up to 40 days. With this form of the disease, it is difficult to answer the question of how long lamblia live in the human body. They parasitize for many years without visible symptoms. The body gradually adapts to them, the disease takes a chronic form.
On a note!
Unattached trophozoites with food masses move into the large intestine. In altered conditions, they are covered with shells, transformed into cysts. In faeces in the open air quickly perish. Cysts remain viable for up to 3-4 weeks.
Hepatobiliary lambliasis
Trophozoites are able to detach from the intestinal wall and for various reasons penetrate into other internal organs. Giardia sensitive to environmental conditions. They instantly die in the bile, are not able to survive in the liver, kidneys or gall bladder. But parasites are found in ducts to these organs. Symptoms of the hepatobiliary form of Giardiasis:
- feeling of bitterness, bile in the mouth;
- yellow bloom on the surface of the tongue;
- dull pain in hypochondrium, lower back;
- regular nausea, vomiting;
- enlarged liver.
Due to the lack of nutrients in the ducts, Giardia does not exist for a long time in such a habitat. However, the proliferation of colonies leads to dysfunction of the bile duct, pancreas. This form of the disease is accompanied in humans by cholecystitis, hepatitis, angiocholitis, liver cirrhosis.
Rare species of giardiasis
Malicious violations of personal hygiene, the practice of non-traditional sexual relations lead to the fact that Giardia live in a person in other internal organs. Giardiasis of this type is difficult to detect, requires complex diagnostics and treatment.
Respiratory system
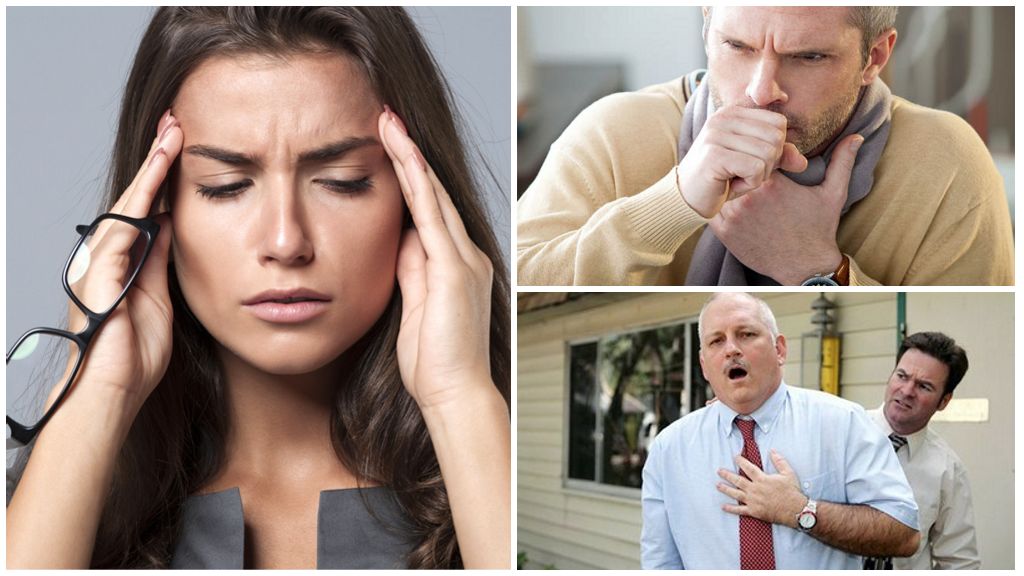
The habitat of Giardia in the body can be the respiratory tract (bronchi, nasopharynx, lungs). Most often, young children are prone to the disease - trophozoites are entered with dirty fingers as a result of self-infection. Symptoms of the disease:
- dry causeless cough;
- swelling in the sinuses, shortness of breath;
- drowsiness, shortness of breath;
- constant dizziness, weakness;
- allergic skin rash;
- gnashing of teeth in a dream, conjunctivitis.
Genitourinary system
With anal sex, the risk of trophozoites entering the urogenital system increases. Giardia parasitic in the genitals, penetrate the renal ducts, master the urinary tract. The disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- sharp pain when urinating;
- heavy discharge from the urinary tract;
- pain in the perineum, anus.
On a note!
In the extraintestinal form of existence, Giardia does not last long. However, the extensive settlement of the parasite colonies leads to infection of the surrounding internal organs (heart, brain). The disease is accompanied by general or complex symptoms (fatigue, decreased performance).
Life expectancy outside the body
Giardia live in the human body indefinitely in the presence of favorable conditions. The optimal environment for active trophozoites is nutrients, lack of oxygen, temperature up to 37⁰С, humidity not less than 80%. Changes in these indicators have a detrimental effect on their viability. At room temperature, trophozoites die outside the human body for 30-60 minutes.
Cysts are resistant to the action of detergents, retain the ability to infection for 3-5 days in a warm environment (up to 20-25⁰С). In the water, their vital activity is delayed for several months. They die in dry air, when the temperature rises to 70 ° C and above. For this reason, one of the effective measures for the prevention of giardiasis is heat treatment - boiling, ironing, steam treatment.