How to determine the presence of Giardia in the human body
Content
- Symptoms of Giardiasis
- Tests for the presence of Giardia
Giardia are common everywhere. On the territory of the Russian Federation, they are present in 35% of the population. Chronic infection causes a systemic immune response and leads to an allergization of the body. In order not to worry about a possible infection, it is necessary to know what indicates the disease and how to detect Giardia in the human body.
Symptoms and infection
Giardia in humans is most often detected by exclusion.The reason for referral to the diagnosis of the disease is the appearance of intestinal symptoms, immune disorders without communication with other infectious or parasitic agents.
Who are the Giardia
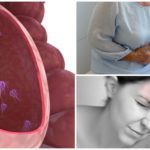
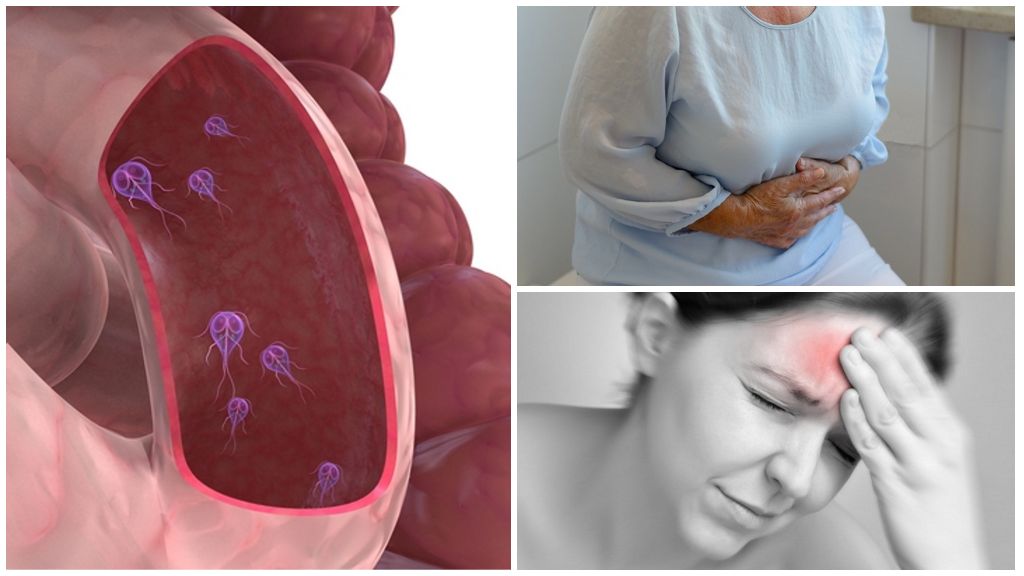
Giardia - flagellate protozoa, penetrating into the body when drinking contaminated water, food, contact with sick people. They inhabit the small intestine, where they are attached directly to its villi and begin to feed at the expense of man. Giardia multiply by dividing in half and can get into the large intestine. In this part of the digestive tract, they turn into the form of cysts with a protective sheath from adverse conditions.
On a note!
With the feces parasites enter the environment. Giardia cysts can remain viable for up to several days. Further development is possible only inside the host.
Signs of Giardiasis
A person can not track the day of infection on the appearance of certain symptoms and determine the presence of Giardia on their own. Parasites have a microscopic size, they can not be seen with the naked eye.
Important!
The incubation period from entering the intestine until the onset of symptoms is from 1 to 3 weeks. The duration of symptoms can be from 1 to 4 weeks.Then giardiasis goes into a chronic course or a person is cured.
To find out the nature of indisposition in a child or an adult, you should consult a doctor if the following symptoms appear:
- diarrhea for more than a week in the absence of fever and other intestinal infections;
- pains in the navel, bloating;
- feeling of weakness, weakness, irritability;
- headaches, dizziness;
- attacks of lowering blood pressure;
- pallor of the skin, blue under the eyes, the appearance of "zade" in the corners of the mouth.
Diarrhea with giardiasis is characterized by the appearance of watery, profuse stool without the addition of mucus or blood.
The child should pay attention to the following symptoms:
- skin allergies (atopic dermatitis);
- exacerbation of bronchial asthma;
- prolonged dry cough;
- tendency to frequent colds.
On a note!
Giardia do not settle in the gallbladder, liver and biliary ducts, but can cause or maintain functional dyskinesia and provoke bile stasis.
Detection of all or part of the symptoms may indicate giardiasis.To understand the reason for their appearance, you should consult an infectious diseases specialist and be examined.
Diagnosis of Giardiasis
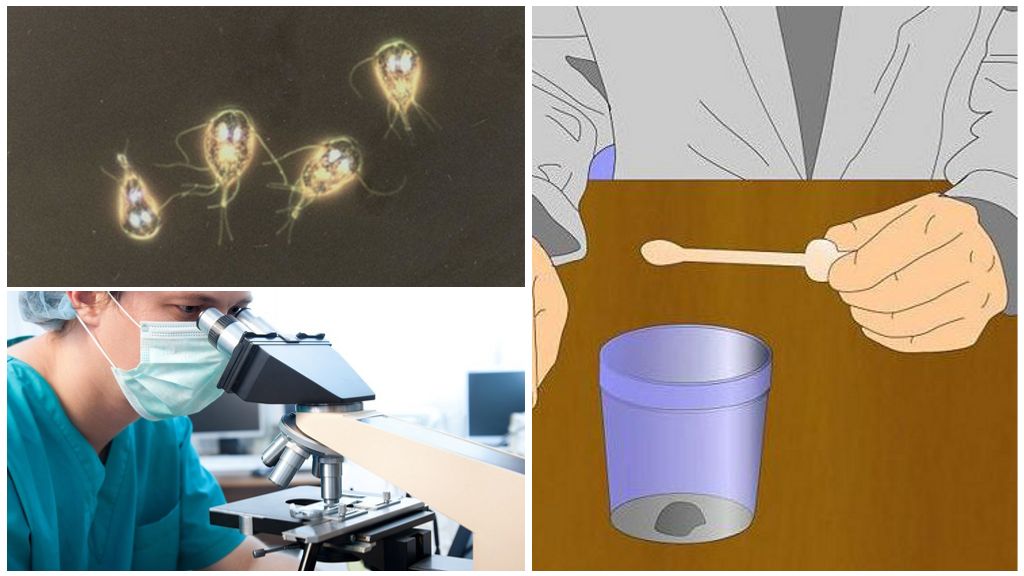
There are several methods for detecting a parasite in the body. For this purpose, blood tests, feces and duodenal contents are used. Other instrumental studies are auxiliary.
Feces
To determine the presence of Giardia in the body, a person suspected of having a disease must have a stool test. In the large intestine, the parasite has the appearance of cysts. This form of Giardia can be detected under a microscope.
To obtain the result, collect the feces in a clean jar, store in the refrigerator and within 6-8 hours from the time of isolation, take it to the laboratory. A positive result will indicate the presence of giardiasis. With a single negative conclusion, the study must be repeated up to 3-4 times, observing all the rules for taking material. Giardiasis may not be recognized in the following cases:
- in a patient receiving treatment for parasites;
- with early taking feces - from 8 to 14 days from the beginning of infection;
- with laboratory diagnosis errors.
For the diagnosis of giardiasis, they also use the method of determining characteristic antigen molecules in the patient's feces. Its effectiveness is higher than conventional microscopy.
For the study, a stool test is taken; special training is not required. A positive result indicates infection with giardiasis, a negative one indicates the health of the patient.
Biopsy of duodenal contents
This method allows you to identify Giardia in adults or children. Its performance is shown to patients in whom the disease was not detected in other ways. To diagnose giardiasis, the contents of the duodenum are placed under a microscope and examined for the presence of parasites and their cysts. This method is considered the most reliable.
Blood test for Giardia
In response to the reproduction of the simplest, immune blood cells begin to produce protein antibodies. Diagnostic value is the detection of total immunoglobulins of classes M and G.
Important!
In order to recognize Giardia, the examination is carried out not earlier than 1-2 weeks after the onset of clinical signs. Otherwise, the antibodies to the parasite will not have time to form, the patient will be deceived by the false-negative result.
One of the clinical symptoms of giardiasis is an increase in the number of eosinophils in the blood test.A biochemical study reveals a decrease in the protein content of gamma-lobulins, albumin, and the growth of the enzyme alkaline phosphatase. These signs only indirectly indicate a parasite in the body and cannot confirm or deny the diagnosis.
Additional examinations
These methods will not allow for the diagnosis of Giardia; they will only help eliminate other diseases and suspect possible infection. Complaints of the patient are often indefinite, the condition is not characterized by bright clinical symptoms.
The patient begins his examination with a visit to the general practitioner. The differential diagnosis of giardiasis will require consultation of other specialists: a dermatologist, a neuropathologist, a pulmonologist, an ultrasound scan of the abdominal organs, with particular attention to the liver and its ducts.
Diagnosis of giardiasis is carried out in the presence of a clinical picture of the disease or symptoms that do not fit into other intestinal infectious lesions. The most reliable methods of detection of the parasite include the study of duodenal contents.