Giardiasis in children: symptoms and treatment
Content
- Forms and life cycle Giardia
- Giardiasis in children
- Means to combat Giardia
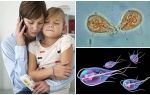
When suspicion of giardia in children, the symptoms and treatment of these parasites interest the parents first. The idea that small bloodsuckers live inside their child horrifies moms and dads, especially young ones. Giardiasis is indeed one of the most unpleasant and sometimes dangerous pathologies.Many modern doctors urge not to panic and not to treat lamblia in children at all with drugs, allowing the body to cope with invasion on its own. But the majority of experts in the field of parasitology believe that giardiasis can cause the pathologies of various organs and systems, so you need to deal with it immediately after the diagnosis.
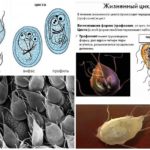
Forms and life cycle Giardia
In children, the causative agent of giardiasis is Lamblia intestinalis or intestinal Giardia. This microorganism from the order of the simplest was first identified in the feces of a patient with diarrhea in 1681. Now giardiasis has the second name, giardiasis, and is classified in ICD 10 as a protozoal intestinal disease under code A 07.1.
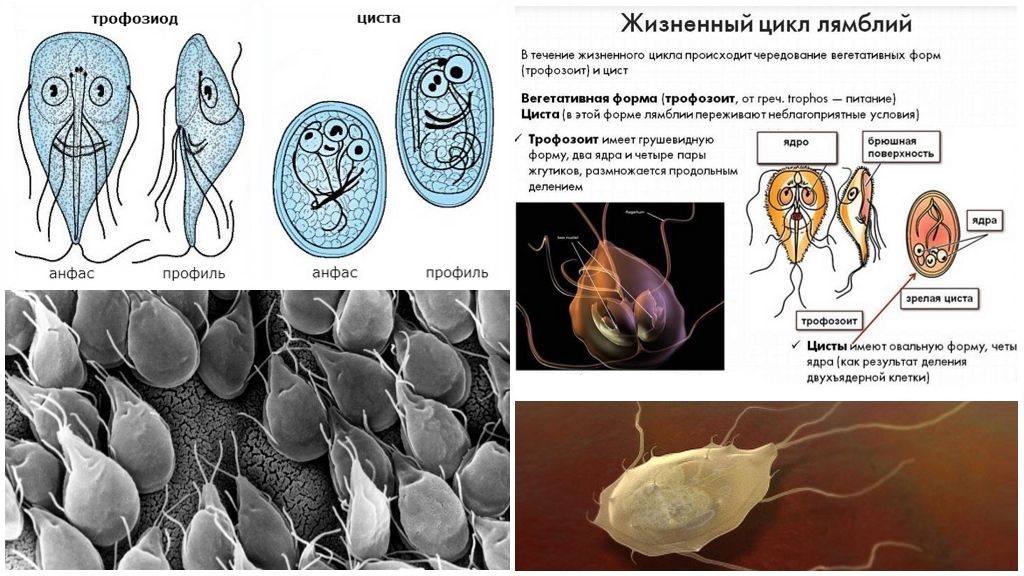
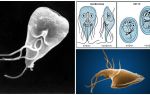
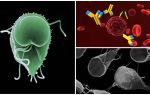
It’s impossible to see how giards look like with the naked eye. You can examine them only under a microscope. Parasites can be in two stages of development, in cystic (sedentary capsules) and vegetative (active trophozoites). This helps them to continue their life cycle.
Mobile forms (trophozoites) have a body in the form of a pear with several pairs of flagella, are able to move, feed in the intestine and multiply.Cysts are needed only for the safe preservation of Giardia in the environment. They are excreted in the fever during peristalsis and persist in adverse conditions for 1 month or longer.
After entering the host's oral cavity, the cysts calmly tolerate the effects of acid in the stomach and open only in the 12 duodenal region. Two new trophozoites appear from each capsule. Further the scheme with reproduction and cyst formation proceeds.
Important!
With the accumulation of a large number of Giardia in the intestines of a child, individuals can penetrate into nearby organs (gallbladder, liver and its ducts).
Ways of infection
Often, parents do not understand where their lamblia come from, because they follow all the standards of sanitation and literally blow away dust particles from a baby. But the cause of infection is not only a violation of hygiene.
The disease has a high level of infectiousness and fecal-oral transmission, which ensures rapid spread in children's groups and in the family circle. In kindergartens and schools, the incidence of giardiasis reaches 70%. Organized children become predominantly between the ages of 2 and 7 years.Infection in this group is more often facilitated by the introduction of cysts into the mouth through dirty hands when playing with a ball or after practicing in the sandbox.
Carriers of Giardia are animals and insects. Cats and dogs cling to cysts on the fur and paws, polluting public places and the hands of the owners. Insects after contact with feces can crawl in food and household items, carrying on their feet thousands of larvae. As a result, the following factors contribute to the spread of giardiasis in children:
- poor hand hygiene;
- infected tap or pond water;
- unwashed fruits, vegetables, and food available to cockroaches and flies;
- infected toys and household items;
- weak immunity and low acidity in the stomach;
- presence of pets.
Many mothers have a bad habit of feeding their offspring right on the street, without prior treatment of their hands. As a result, the children carry lamblia cysts into the mouth with cookies or candy.
On a note!
Another factor of infection is the tendency to bite your nails or suck your fingers. It is usually present in a child 2 years or younger due to early weaning from the breast or nipple.Parents often ignore this habit, whereas according to statistics such lamblia appear in almost 100% of such babies.
In medical practice, there are cases of diagnosing lamblia, even in infants. This often contributes to the poor handling of baby toys and poor hygiene of the hands of parents. The danger of the disease at this age lies in a weak immune status and problems with the selection of drugs from Giardia. Treatment of parasites in infants can cause many side effects.
Adolescents and children older than 7 years, too, often suffer from giardiasis, but their immune system is more resistant and the disease is often hidden. Sometimes it is possible to find out about the infection by chance while passing a physical examination or treating a comorbid pathology. In adolescents, the main cause of infection is the habit of snacking after school without first washing your hands. Frequent manifestations of giardiasis in this group are acne on the face, which many take for peculiarities of puberty and treat incorrectly.
Important!
One carrier of giardiasis per day can emit hundreds and thousands of cysts, as a result of which an entire school class or a kindergarten group becomes infected.
Clinical picture
Symptoms and treatment of giardiasis in children are closely interrelated.The more severe the invasion, the brighter the clinical picture and the more complicated the therapy. The degree of manifestation of typical signs of Giardia depends on the age category and the state of the immune system.
Giardiasis can be acute or chronic, have a latent or pronounced course. Due to the absence of specific symptoms of Giardia in children, the disease is often mistaken for allergies, poisoning and other pathologies. This contributes to the reproduction of parasites and can provoke their entry from the intestine into the hepatic ducts. Treatment in this case is complicated.
Acute form of giardiasis
It develops more often when lamblia are ingested by young children. The source of infection is parents or other family members. The child begins to scream and presses the legs to the stomach, his face and eyes itch. The state is accompanied by:
- low-grade fever;
- gas and flatulence;
- nausea and regurgitation;
- paroxysmal abdominal pain;
- diarrhea;
- the appearance of a rash on the body of the type of urticaria.
Microscopic worms are not visible in the feces, but can change the nature of feces. First, the feces become frothy,and later, without treatment, they get a fetid odor. The condition may be replaced by periods of well-being, followed by repeated attacks.
On a note!
Symptoms of giardiasis in children should be differentiated from intestinal infections and allergies that require specific treatment.
Chronic form
More often diagnosed in adolescents and children over 7 years old. Occurs with periods of unreasonable nausea and loss of appetite. The child often complains that his stomach hurts and his stool is broken. A tongue appears on the tongue, there is a smell from the mouth, the palms and feet become yellowish. Children are tormented by lamblia coughing, which indicates an allergic reaction to the parasites' waste products. Treatment of this form should be comprehensive.
Complications
With prolonged disregard for the signs of giardia in children, individuals become dangerous. They multiply massively and cause intoxication of the whole organism. A child may complain of heart pain, weakness and headache. Parents also note:
- increased irritability;
- sleep disturbance;
- weight changes (weight loss or obesity);
- decreased immunity and, as a consequence, frequent infections of the throat and nose;
- stomach ache.
Among the rare complications is infection of the urogenital system. With dirty laundry, parasites can enter the ureters. As a result, it is possible to detect Giardia in the urine when conducting a general analysis. The consequence of such localization is cystitis and urethritis.
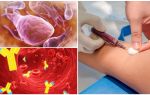
Diagnostics
The first stage of diagnosis is an external examination of the child and history taking. The doctor draws attention to the physique, color of the skin and mucous membranes. It is important to identify the infection factor and eliminate the source of infection. Each case of giardiasis is registered in the sanitary-epidemiological structures.
On a note!
To finally identify a parasitic disease, it is necessary to pass feces and blood for analysis. The feces in the diagnosis Giardia should be attributed to the laboratory in the morning immediately after a stool. Not only cysts, but also trophozoites can be found in warm feces.
If the result is negative, the analysis is repeated twice more. If the clinic is maintained, and giardiasis is not confirmed, an immunological study is prescribed. Antibodies to Giardia in the blood can be determined by ELISA. There is also a highly sensitive PCR assay. It allows you to detect the DNA of parasites at the cellular level.
Treatment methods
For the treatment of Giardia in children, there are a number of drugs. Therapy is carried out at home, hospitalization is not required. Giardia is treated by a parasitologist, infectious disease specialist or pediatrician. Means are dosed depending on the weight or age of the child.
To help Giardia help drugs from the antiprotozoal pharmacological group.
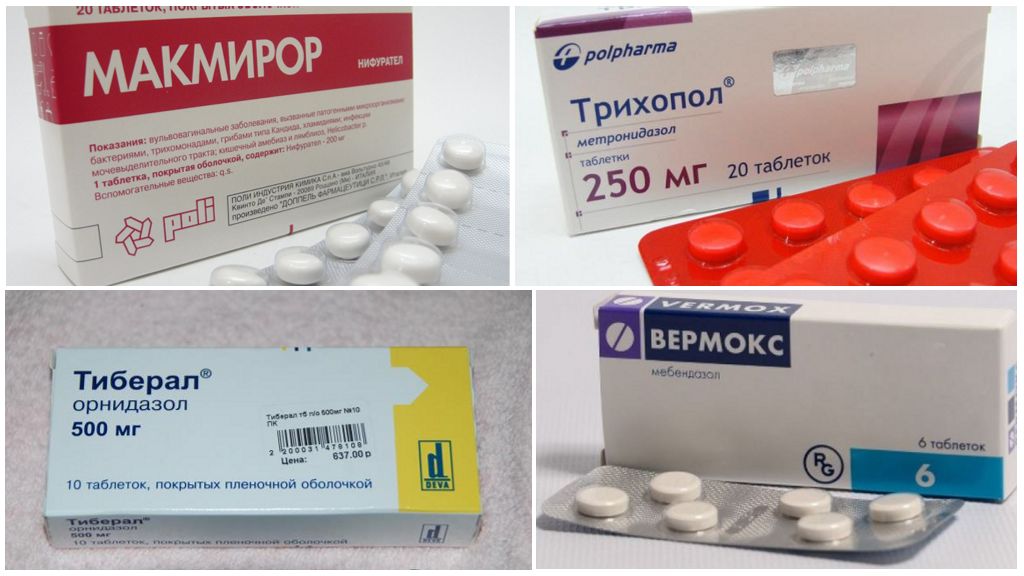
| Remedy for treatment | Application features |
|---|---|
| Tiberal | When the child weighs up to 35 kg, no more than 40 mg is prescribed per 1 kg. If the weight is greater, the dosage is 1500 mg. In order to get rid of giardiasis, treatment with a single application is sufficient. |
| Macmiror | It is necessary to give the baby tablets 2 times a day at a dosage of 15 mg per kg of weight. Lamblia can be removed in 1 week. |
| Metronidazole or Trichopol | Treat lamblia metronidazole should be at least 5 days. Dosage for the treatment of babies up to the year 0, 125 g, from 2 to 8 years old from 0, 25 to 0, 375 g 2 times a day. |
| Vermox | Helps to cure Giardia in 5 days. Take one tablet per day. The dosage is the same for children from 2 to 12 years. |
During the treatment of giardiasis in children it is necessary to follow a diet with restriction of spicy dishes, sweets, flour and fat.Therapy is prescribed to all family members. After the course of treatment it is necessary to pass control tests. Use folk recipes in children should be with caution, after consulting with a doctor.
Important!
To use folk remedies can only be used in conjunction with medical treatment or in order to prevent infection.
Prevention
Exclude from the life of a child all the factors contributing to infection is impossible. But taking into account the peculiarities of the fecal-oral transmission, it is sufficient to interrupt the chain of the life cycle of Giardia, avoiding the entry of cysts in the mouth. To do this, follow simple preventive measures and make sure that the kids do not lick their fingers and do not pull toys or foreign objects into their mouths. A 3-year-old child should clearly form a habit of washing hands before eating and after using the toilet.
For the prevention of Giardia and hygiene in younger children, only parents are responsible. They should first of all monitor the cleanliness of their hands and prevent the infection from getting into the baby’s mouth, so that they do not poison it with toxic drugs for the treatment of worms.