Head lice
Content
- Head lice
- Linen lice
- Head lice
- Lice and nits
- Nits
- Lice in hair
- Aerosol Vapor Plus
- Means Nuda
Lice on the head were parasitic among the ancient people, who shared their shelter from the weather with wild animals and bats. It was these warm-blooded bats that caused the parasites to settle. Giant Saurodectes parasitized pterosaurs from the early Cretaceous. After the death of the dinosaurs, the lice adapted themselves to the new food objects and settled with the bats in the caves.
Description and brief characteristic of the form
Changing the power object, lice and transformed themselves. In the process of evolution, they significantly decreased in size and lost wings. Insects began to differentiate about 130–115 million years ago, since it was in the sediments of this period that wingless lice were found. Lice are highly specialized parasites and cannot change their host.
Interesting!
Scientists from the University of Illinois (USA) described the adaptive traits of lice parasitic on different types of animals and birds. Do birds or chicken lice a long narrow body that helps them hide in feather beads, while insects living in the fur of rodents have an oblong recess on their heads, which they “fasten” to the hairs.
In humans, human lice cause infection, which have two morphotypes — head lice and pubic ploshchitsy. They differ in appearance and are adapted to the type of hairs on different parts of the body. Head lice have a subtype - cootie. From the wardrobe, head lice differ more shortened body and color - more gray.
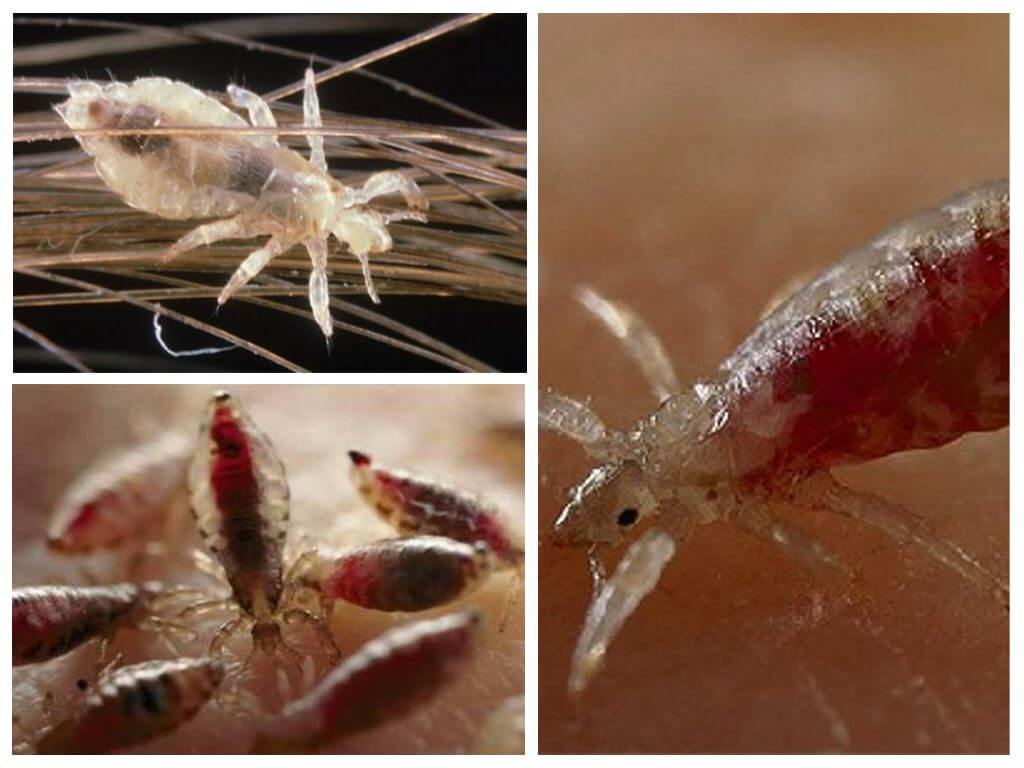
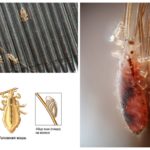
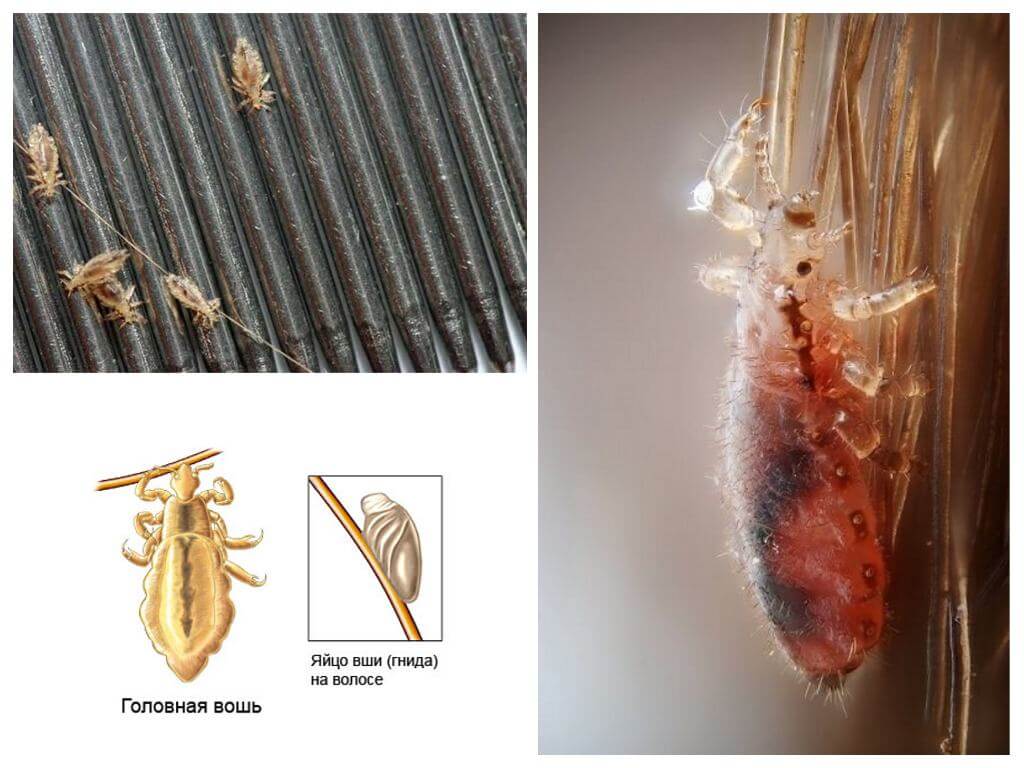
The elongated body of the head lice is clearly divided into the head and abdomen. The abdomen is much larger than the cephalothorax. After sucking a portion of blood, the color of the abdomen changes - it becomes red. The long body allows the parasite to quickly move among the dense hairline on the head. A tiny, 2 to 4 mm, dimensions make it elusive.
Interesting!
Body and head lice can mutually turn when changing habitat. These morphotypes were divided and specialized only 72 ± 42 thousand years ago. Getting into the folds of underwear, head lice after several generations acquire the characteristic features of body lice. Despite the close proximity, in nature they do not interbreed, but in the laboratory they give offspring capable of breeding.
Six running limbs provide fast movement. Paws end in large claws in the form of sickles. With their help, head lice cling to the hairs. Covering the hair, claw tightly pressed to the lower leg, securely fixing the insect. It is these claws that are adapted to covering a hair of a certain cross section, which do not allow the parasite to live on the pubic hair or in the armpit hair, the beard - there is thicker hair.Anthony van Leeuwenhoek, who is being quoted today by biology textbooks, admired the structure and functionality of lice claws.
Type and organs of nutrition
The parasite's oral apparatus is ideally suited for blood supply. Two sharp stiletto hidden in a soft tube, turning outwards, pierce the skin. At the distal end of the tube there is a nimbus of small hooks, with the help of which the head louse is attached to the skin, sucking blood.
When the insect does not drink blood, the "proboscis" is hidden in the head section. In the proboscis open ducts of highly developed salivary glands. At louse bite their secret enters the capillary in the scalp, preventing the formation of a blood clot. Once in the wound, saliva irritates the tissue, causing itching.
When feeding, head lice suck out about 0.5 ml of blood at one time, and these “approaches” make parasites 4-5 during the day. Like all insects with incomplete transformation, the nymphs of head lice are competitors of adults in the diet - they also suck blood.
Interesting!
Head lice feed only on human blood. While receiving the vaccine for typhus, the material for which was taken from infected insects,The question “how to feed the head lice?” arose sharply. However, scientists struggled, offering laboratory animals to parasites, trying to feed them with the help of ingenious devices - head lice were persistent in their preferences. Researchers had to look for volunteers who agreed on their heads to feed ahead.
Scientists have established another feature of the power of parasites - head lice prefer the blood of girls aged 6-10 years. This feature was noted by Aristotle. In his essay “Problemata”, the great philosopher makes incorrect conclusions from correct observations, including the reasons for such selectivity.
With the invention of the microscope, scientists began to study in detail the internal structure of synanthropic insects. P. Borel, a physician at the court of Louis XIV, King of France, described his observations in the following way: "A terrible transparent louse makes it possible to observe how blood circulates in her heart."
The life cycle of the parasite
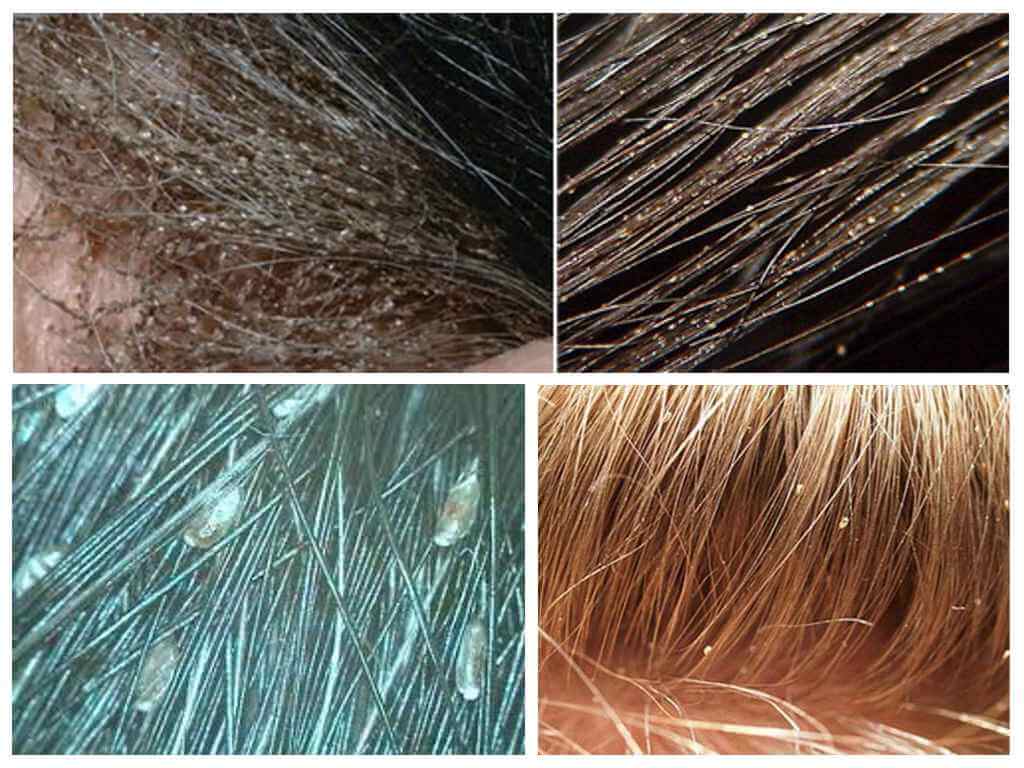
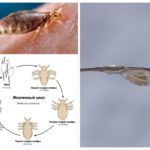
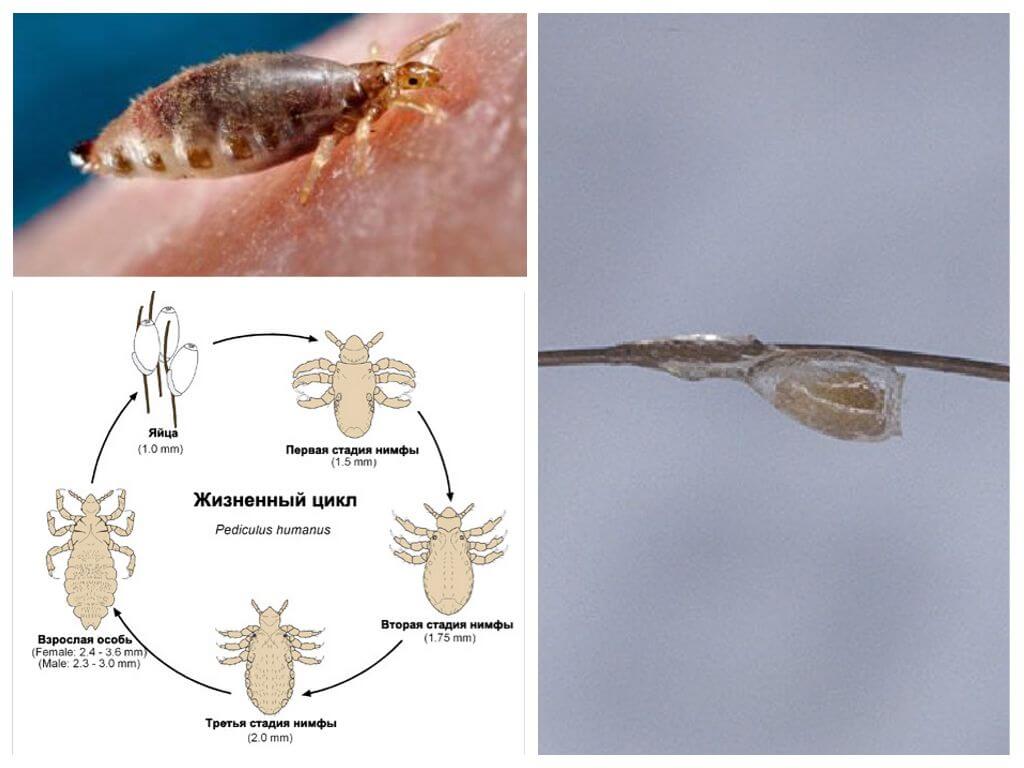
Having reached puberty, the female lays on the hair of the head up to 5 eggs per day. For the whole period of life, which in adult head lice is 30 days, the population increases by 150 individuals. Eggs are oval, covered with a dense shell, called nits. This name gave them Aristotle.With the advent of the microscope, Aristotle’s idea of spontaneous lice was refuted.
Under the microscope, sex differences in head lice are visible - a split in the last segment of the abdomen in the male, which the female does not have. The male copulatory organ is hidden inside the body and shines through the abdomen in the form of an elongated triangular formation. On the front pair of the male's paws there are claws, which he uses when mating to hold the female partner.
Sexual intercourse of head lice lasts 20-70 minutes. During mating, the male introduces seed material, which can be stored for a long time in the abdomen of the "lady". Already formed and covered with a dense shell of the egg, moving through the oviduct to the exit. In the cap there are many tiny holes, through which the male sex cells penetrate and fertilize them.
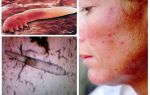
The female attaches the nits with the help of the gluey secretion of special glands in the root part of the hair. Here, the temperature of a person’s head accelerates the ripening process of eggs. How do lice and nits on the head, clearly demonstrates the photo. From the nits after 7-10 days, the larvae come out, very similar to their parents, but much smaller in size.The larva feeds heavily, grows, sheds several times and in 6-10 days turns into an imago. Thanks to such short maturity of eggs and the rapid growth of larvae, lice breeding happening at a rapid pace.
Head lice very sensitive to temperature - the whole life cycle of the parasite depends on it. At normal human body temperature (36-37 ° C) the development of nits takes 4-8 days. A decrease in temperature by 13 ° C slows down the development of the embryo by half. The lower limit of the temperature "comfort zone" is 22 ° C, and the upper - 40 ° C.
Interesting!
When the temperature drops to + 12 ° С, females stop laying eggs, the parasite activity decreases. At temperatures below 10 ° C, insects leave the head of the host and crawl in search of more comfortable conditions. The Bible contains a description of the death of King Herod, from whose corpse "lice flowed like a spring that flows from the earth." And in the annals such historical evidence of the death of the Bishop of Noyon is given: “there were so many lice on it that when he died, he had to be sewn into a leather bag so that the lice would not spread before they were buried by the grieving guests”.In those days, Christians had lice was a sign of holiness, indicating the killing of the flesh.
Despite the "attachment" to the object that provides food, the parasites leave it when the opportunity arises, expanding the area of distribution.
Ways of infection
Lice on the head of a person have long ceased to be a sign of a marginal personality. Increased attention to personal hygiene, hair care for the head, the use of ammonia hair dyes and the emergence of such powerful insecticides as DDT for a few decades allowed a person to breathe a sigh of relief. But in the 70s of the 20th century the first alarm came from England. Here, when examined in the head, lice and nits were found in 13-17% of adolescents. A wave of winding swept across Europe and swept the United States.
Scientists put forward various versions, ranging from long-haired youth that was fashionable at the time and ending with a change in the biology of parasites and the formation of resistance. But the only reason for which the "disease of vagrants" has become a national problem, so put forward and was not.
Head louse is not very worried about the cleanliness and neatness of the object.Close contact with an infected person, clothing, bedding. lice are transmitted to another person who has made contact. Therefore, epidemics of lice infestation are often found in close teams - schools, kindergartens, summer camps, sanatoriums.
Interesting!
Lice in the water can live for about 2 days, so people get infected by swimming in a pool or an open pond. Outside its host, the parasite can live up to 2 days, and at a temperature of about 10 ° C - up to 10 days. Removed from the hair of a parasite in a hurry to return to his master. Lice are very "like" clean, shampooed baby hair. Here it is easier for them to feed by piercing thin skin, freed from the horny scales of the epidermis, sebum, and dirt.
The rate of reproduction of head lice also depends on the degree of lumpiness. The more parasites on the human head, the less insects spend time searching for a partner for mating.
Symptoms of Pediculosis
Pediculosis is the body's response to lice bites. Head lice is manifested:
- itching;
- erythema occurs on the surface of the skin in the places of bites - swelling and redness, small bluish spots;
- visible yellowish crusts;
- bites can cause inflammation of the hair follicles on the head;
- the introduction of a secondary infection in the areas of damage to the epidermis causes dermatosis, fungal diseases of the scalp.
Visually inspecting the scalp, empty shells of eggs and nits are visible in the hair. Untreated pediculosis is accompanied by inflammation of the regional lymph nodes on the head and neck, allergic dermatitis, furunculosis, conjunctivitis.
From the moment of infection with head lice until symptoms of pediculosis may take several weeks. It is easy to detect parasites - the nits on the hair are clearly visible in any light and do not need special tools to detect them.
Pediculosis treatment
To get rid of lice The pharmaceutical industry produces a variety of means to combat insects on the hair of the head:
- For the treatment of pediculosis in adults use products containing insecticides - emulsions Medyfox, Medilis-Super, Pedilin shampoos, HygiaPediculen-Ultra spray, Aerosol Vapor Plus, cream nix.
- Many drugs are based on liquid silicone. They are safe for the human body, so these medicines are recommended for removing lice in children. This group of drugs includes Nuda spray, Paranit-Sensitiv.
- Against lice use preparations based on vegetable, mineral, essential oils - sprays AvalanchePediculen-ultra.
- In addition to the insecticide complex, the combined agents include natural acids - Bubil, Spray Pax, A-steam, Paraplus. Means additionally care for the scalp and hair.
Despite the fact that pediculicidal drugs effective and quickly get rid of the problem, they do not act on nits, so the treatment must be supplemented by combing the hair. To do this, use a special comb with fine pitch metal corrugated teeth. Comb lice may be electric, while combing the electric discharge affects living lice on the head. To completely get rid of pediculosis, re-treatment is necessary after 7-10 days, during the period when nymphs emerge from nits.
Disinsection of women in the period of gestation or lactation and children require a special approach and selection of special means. Safe medications that improve the condition of hair on the head and effectively fight head lice - NOC, Nittifor, Nuda, Paranit, Lavinal and others.
Many patients prefer not to use "chemistry". For them there are folk remedies for head lice:
- vinegar solution;
- cemerica water;
- decoctions of pomegranate and lemon balm;
- essential oils: ylang-ylang, cloves, anise, tea tree ;
- homemade ointment from wild rosemary, cranberries, hellebore;
- fruit and berry acids;
- tar soap.
Modern methods pediculosis treatment should not reject the experience of past generations, accumulated in the "bloody" fight against insects that have gone with a man all the way from primitive man to reasonable man.